14 3/8 As A Decimal
horsecheck
Sep 22, 2025 · 5 min read
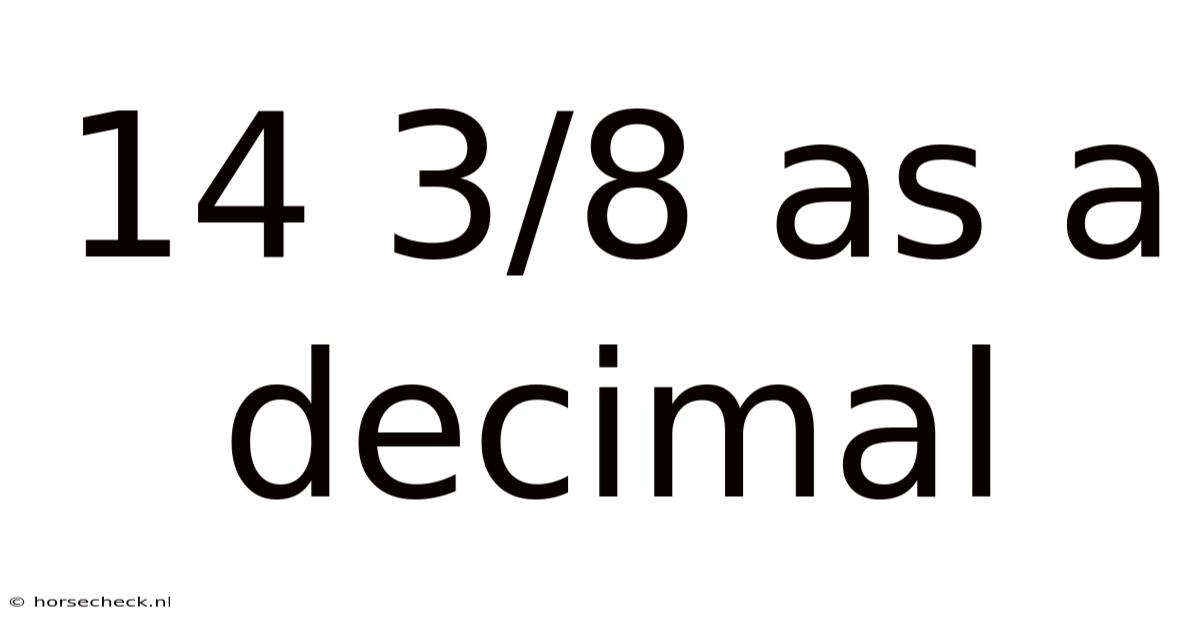
Table of Contents
14 3/8 as a Decimal: A Comprehensive Guide
Converting fractions to decimals is a fundamental skill in mathematics, crucial for various applications from everyday calculations to advanced scientific computations. This comprehensive guide delves into the process of converting the mixed number 14 3/8 into its decimal equivalent, providing a step-by-step approach, explaining the underlying principles, and addressing frequently asked questions. Understanding this conversion not only strengthens your mathematical foundation but also enhances your ability to work confidently with different number systems.
Understanding Mixed Numbers and Fractions
Before we dive into the conversion, let's solidify our understanding of mixed numbers and fractions. A mixed number combines a whole number and a fraction, like 14 3/8. The whole number (14 in this case) represents the complete units, while the fraction (3/8) represents a portion of a unit. A fraction, in its simplest form, expresses a part of a whole. The numerator (3) represents the number of parts we have, and the denominator (8) represents the total number of equal parts the whole is divided into.
Converting 14 3/8 to a Decimal: The Step-by-Step Method
There are several ways to convert 14 3/8 to a decimal. The most straightforward method involves two simple steps:
Step 1: Convert the Fraction to a Decimal
To convert the fraction 3/8 to a decimal, we perform a simple division: divide the numerator (3) by the denominator (8).
3 ÷ 8 = 0.375
Step 2: Combine the Whole Number and the Decimal
Now, we simply combine the whole number part (14) with the decimal equivalent of the fraction (0.375).
14 + 0.375 = 14.375
Therefore, 14 3/8 as a decimal is 14.375.
Alternative Methods: Expanding Our Understanding
While the above method is efficient and widely used, let's explore alternative approaches to deepen our understanding of the conversion process:
Method 1: Converting to an Improper Fraction First
This method involves first converting the mixed number into an improper fraction, then converting the improper fraction to a decimal.
-
Convert to an Improper Fraction: To convert 14 3/8 to an improper fraction, we multiply the whole number (14) by the denominator (8), add the numerator (3), and keep the same denominator (8).
(14 * 8) + 3 = 115
The improper fraction is 115/8.
-
Convert to a Decimal: Now, divide the numerator (115) by the denominator (8).
115 ÷ 8 = 14.375
This again confirms that 14 3/8 as a decimal is 14.375.
Method 2: Using Long Division Directly
While less efficient for simple fractions, understanding long division is crucial for more complex fraction-to-decimal conversions. Let's perform long division on 14 3/8:
- We initially deal with the whole number, 14. This remains as 14.
- Next, we focus on the fraction 3/8. We set up the long division problem: 3 ÷ 8.
- We add a decimal point and zeros to the dividend (3) to facilitate the division.
- We perform the division step-by-step, determining how many times 8 goes into 30, 300, and so on.
This long division process will eventually yield the same result: 0.375. Combining this with the whole number 14 gives us 14.375.
The Significance of Decimal Representation
The decimal representation of 14 3/8, which is 14.375, provides several advantages:
- Ease of Comparison: Decimals are easier to compare than fractions, particularly when dealing with multiple numbers. For example, comparing 14.375 with other decimals is simpler than comparing 14 3/8 with other fractions.
- Computational Efficiency: Many calculations, especially those involving multiplication and division, are more straightforward with decimals.
- Wider Applicability: Decimals are widely used in various fields, including science, engineering, finance, and everyday life.
Practical Applications of Decimal Conversions
The ability to convert fractions to decimals finds its application across numerous fields:
- Finance: Calculating interest rates, discounts, and profits often involves decimal representations.
- Engineering: Precise measurements and calculations in blueprints and design require decimal accuracy.
- Science: Scientific data and measurements are usually expressed in decimals for clarity and consistency.
- Cooking and Baking: Recipe adjustments and ingredient measurements benefit from the precision of decimals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Can all fractions be converted to terminating decimals?
No. Fractions with denominators that have prime factors other than 2 and 5 (when simplified) result in non-terminating, repeating decimals. For example, 1/3 converts to 0.333..., a repeating decimal. However, 3/8 has a denominator (8) whose prime factorization is 2³, thus resulting in a terminating decimal.
Q2: What if the fraction is negative?
If the mixed number is negative, such as -14 3/8, the decimal equivalent will also be negative: -14.375. The conversion process remains the same, but the negative sign is retained.
Q3: How can I check my answer?
You can check your answer by converting the decimal back to a fraction. For 14.375, we can convert this to an improper fraction and then a mixed number to verify. 14.375 = 115/8 = 14 3/8.
Q4: Are there any online tools for converting fractions to decimals?
Yes, many online calculators and converters are readily available. However, understanding the underlying process is crucial for mathematical proficiency.
Conclusion
Converting 14 3/8 to its decimal equivalent, 14.375, is a straightforward process that demonstrates a crucial concept in mathematics. Understanding the different methods—direct division, conversion to an improper fraction, and long division—reinforces the underlying principles and allows for more versatile problem-solving. The significance of decimal representation extends across various disciplines, highlighting its practical importance in daily life and professional fields. The ability to confidently perform this conversion signifies a strong foundation in fundamental mathematical skills. Mastering this skill not only enhances mathematical understanding but also opens doors to more complex mathematical concepts and their practical applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
175 Deg C To F
Sep 22, 2025
-
What Is 9 Times 7
Sep 22, 2025
-
What Is 3 Of 7
Sep 22, 2025
-
2 9 In Simplest Form
Sep 22, 2025
-
9 1 100 As A Decimal
Sep 22, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 14 3/8 As A Decimal . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.