140 Deg F To C
horsecheck
Sep 24, 2025 · 6 min read
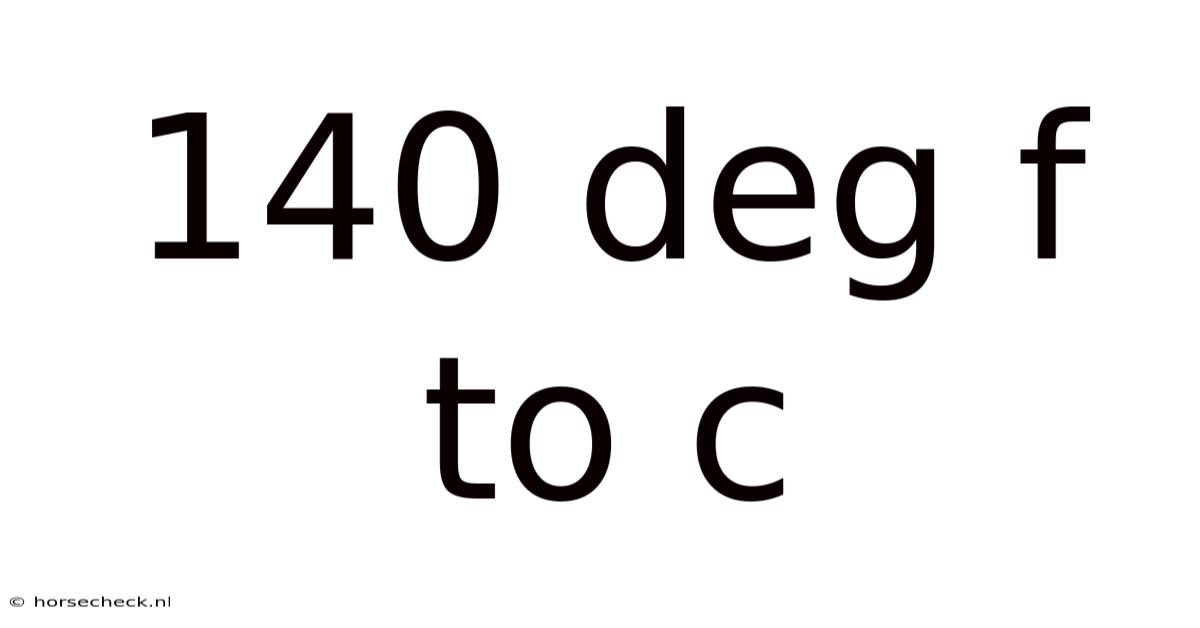
Table of Contents
140°F to °C: Understanding Temperature Conversions and Their Applications
Converting temperatures between Fahrenheit (°F) and Celsius (°C) is a fundamental skill in many fields, from cooking and baking to science and engineering. This comprehensive guide will not only show you how to convert 140°F to °C but also delve into the underlying principles, practical applications, and frequently asked questions surrounding temperature conversions. Understanding these conversions is crucial for accurate measurements and effective communication across various disciplines. Let's dive in!
Understanding the Fahrenheit and Celsius Scales
Before we calculate 140°F to °C, it's essential to understand the two temperature scales involved.
-
Fahrenheit (°F): This scale, developed by Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit in the early 18th century, sets the freezing point of water at 32°F and the boiling point at 212°F, with a difference of 180 degrees between them. It's primarily used in the United States and a few other countries.
-
Celsius (°C): Also known as the centigrade scale, Celsius was developed by Anders Celsius. It defines the freezing point of water as 0°C and the boiling point as 100°C, with a 100-degree difference. It's the most widely used temperature scale globally and is the preferred scale in scientific contexts.
Converting 140°F to °C: The Formula and Calculation
The conversion between Fahrenheit and Celsius is straightforward, using the following formula:
°C = (°F - 32) × 5/9
Let's apply this formula to convert 140°F:
°C = (140 - 32) × 5/9 °C = 108 × 5/9 °C = 60
Therefore, 140°F is equal to 60°C.
Practical Applications of 140°F (60°C) Temperature
A temperature of 140°F (60°C) holds significance in various applications:
-
Food Safety: This temperature is crucial in food safety practices. Maintaining food at or above 140°F (60°C) helps prevent the growth of harmful bacteria, ensuring food safety. This is particularly important during food preparation, storage, and service in commercial kitchens and food processing plants. Failing to maintain this temperature can lead to foodborne illnesses.
-
Baking and Cooking: Many recipes, particularly those involving sauces, custards, and certain types of candy, require precise temperature control. 140°F (60°C) might be a crucial point in a recipe, for instance, to achieve a specific texture or prevent curdling.
-
Industrial Processes: In various industrial processes, maintaining a consistent temperature is vital. 60°C might be a critical temperature in chemical reactions, material processing, or manufacturing processes, requiring precise temperature regulation and monitoring equipment.
-
Medical Applications: In some medical procedures or applications, controlling temperature is crucial for patient safety and the effectiveness of the procedure. While 60°C is usually too high for direct body contact, maintaining equipment or solutions at this temperature might be necessary in certain specialized medical contexts.
-
Agriculture and Horticulture: Optimum growing temperatures for specific plants can vary significantly. Understanding and controlling temperature through greenhouses or other means is essential for maximizing yield and preventing crop damage. 60°C could be a significant temperature threshold for some plants, determining whether they thrive or suffer heat stress.
Beyond the Conversion: Deeper Understanding of Temperature
While the conversion itself is simple, understanding the underlying principles provides a deeper appreciation for the process. Here’s a look at some key aspects:
-
Linear Relationship: The relationship between Fahrenheit and Celsius is linear, meaning that a constant change in one scale corresponds to a proportional change in the other. This allows us to easily convert between the two scales using the formula.
-
Different Zero Points: The key difference between the two scales lies in their zero points. Celsius uses the freezing point of water (0°C) as its zero point, while Fahrenheit uses a different arbitrary point. This difference is factored into the conversion formula.
-
Different Degree Sizes: The size of a degree is also different between the two scales. The difference between the freezing and boiling points of water is 100 degrees in Celsius and 180 degrees in Fahrenheit. This difference is why the 5/9 factor is included in the conversion formula.
Understanding Temperature Measurement Tools
Accurate temperature measurements are essential for reliable conversions. Various tools are available, each suited to different applications:
-
Thermometers: These come in various types, including liquid-in-glass thermometers, digital thermometers, and thermocouples, each with different levels of accuracy and suitability for specific temperature ranges.
-
Temperature Sensors: These electronic sensors provide accurate and often real-time temperature readings, crucial for applications requiring continuous monitoring and precise control, such as industrial processes or scientific experiments.
-
Infrared Thermometers (Non-contact): These allow for temperature measurement without direct contact, ideal for measuring the temperature of surfaces or objects that are difficult or unsafe to touch.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Why are both Fahrenheit and Celsius still used?
A1: The continued use of both scales is largely due to historical reasons and regional preferences. While Celsius is the internationally preferred scale for scientific and most global applications, Fahrenheit remains prevalent in the United States for everyday use and some specific industries.
Q2: Are there other temperature scales besides Fahrenheit and Celsius?
A2: Yes, there are other temperature scales, such as Kelvin (K), which is an absolute temperature scale used in scientific applications, where 0 K represents absolute zero. There's also the Rankine scale, which is an absolute scale based on Fahrenheit degrees.
Q3: How accurate are temperature conversions?
A3: The accuracy of temperature conversions depends on the accuracy of the initial temperature measurement. Using precise measuring tools and applying the conversion formula correctly ensures a highly accurate result. Minor discrepancies might arise due to rounding errors.
Q4: What are some common mistakes when converting temperatures?
A4: Common mistakes include forgetting to subtract 32 from the Fahrenheit temperature before multiplying by 5/9 or using the incorrect formula entirely. Double-checking your calculations is always advisable.
Q5: Can I use online converters for temperature conversions?
A5: Yes, many online converters are readily available. However, understanding the underlying formula is crucial for understanding the process and ensuring accuracy, especially in situations requiring precise calculations.
Conclusion: Mastering Temperature Conversions
Converting 140°F to 60°C, as demonstrated above, is a simple yet essential skill. Understanding the underlying principles, the practical applications, and the tools involved allows for accurate and reliable temperature measurement and conversion across various contexts. Whether you're a chef perfecting a recipe, a scientist conducting an experiment, or an engineer managing an industrial process, mastering temperature conversions is key to success. Remember to always double-check your calculations and utilize appropriate measuring tools to ensure accuracy. The information presented here provides a solid foundation for understanding temperature conversions and their widespread applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Are Factors For 36
Sep 24, 2025
-
31 8 As A Decimal
Sep 24, 2025
-
Lcm Of 56 And 84
Sep 24, 2025
-
1 3 As Mixed Number
Sep 24, 2025
-
3 8 Percent As A Decimal
Sep 24, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 140 Deg F To C . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.