15 16 As A Decimal
horsecheck
Sep 17, 2025 · 5 min read
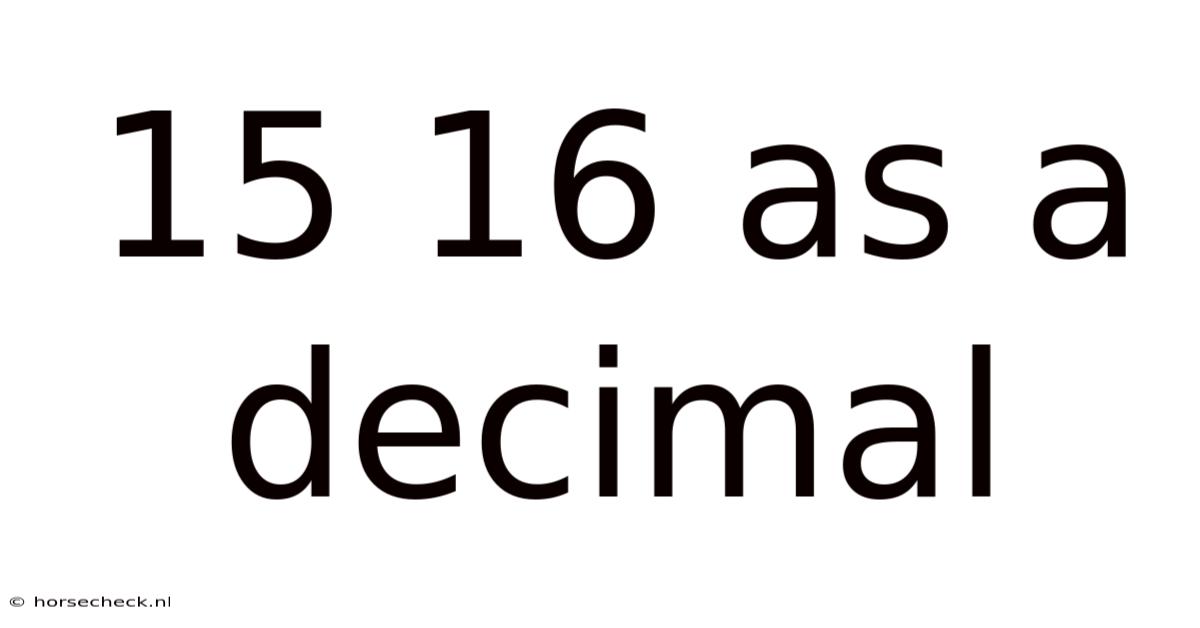
Table of Contents
Decoding 15/16 as a Decimal: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding fractions and their decimal equivalents is a fundamental skill in mathematics. This article will delve deep into converting the fraction 15/16 into its decimal form, exploring various methods and providing a clear, step-by-step explanation. We will also touch upon the practical applications of this conversion and address common questions surrounding decimal representation. This guide is designed for students, educators, and anyone seeking a comprehensive understanding of fraction-to-decimal conversion. By the end, you'll not only know the decimal equivalent of 15/16 but also grasp the underlying principles.
Understanding Fractions and Decimals
Before we dive into converting 15/16, let's briefly revisit the concepts of fractions and decimals. A fraction represents a part of a whole, expressed as a ratio of two numbers: the numerator (top number) and the denominator (bottom number). A decimal is another way to represent a part of a whole, using a base-ten system where numbers to the right of the decimal point represent tenths, hundredths, thousandths, and so on.
The key to converting a fraction to a decimal lies in understanding that the fraction represents a division problem. The numerator is divided by the denominator.
Method 1: Long Division
The most straightforward method to convert 15/16 to a decimal is through long division. This method involves dividing the numerator (15) by the denominator (16).
-
Set up the long division: Write 15 inside the long division symbol (÷) and 16 outside.
-
Add a decimal point and zeros: Since 15 is smaller than 16, we add a decimal point after 15 and append zeros as needed. This doesn't change the value of 15, but allows us to continue the division process.
-
Perform the division: Begin the long division process. 16 goes into 15 zero times, so we place a 0 above the decimal point. Then, consider 150. 16 goes into 150 nine times (16 x 9 = 144). Subtract 144 from 150, leaving a remainder of 6.
-
Bring down the next zero: Bring down the next zero to make 60. 16 goes into 60 three times (16 x 3 = 48). Subtract 48 from 60, leaving a remainder of 12.
-
Continue the process: Bring down another zero to make 120. 16 goes into 120 seven times (16 x 7 = 112). Subtract 112 from 120, leaving a remainder of 8.
-
Repeat until desired accuracy: Continue this process until you reach the desired level of accuracy. In this case, we'll continue for a few more steps. Bring down a zero to make 80. 16 goes into 80 five times (16 x 5 = 80). The remainder is 0, so the division is complete.
Therefore, 15/16 = 0.9375.
Method 2: Using a Calculator
A simpler, quicker method is to use a calculator. Simply divide 15 by 16. The calculator will directly provide the decimal equivalent: 0.9375. This method is especially useful for more complex fractions.
Method 3: Understanding Decimal Place Values
This method helps in understanding the relationship between the fraction and its decimal representation. We can think of 15/16 as 15 parts out of a possible 16. To convert this to a decimal, we need to find an equivalent fraction with a denominator that is a power of 10 (10, 100, 1000, etc.). However, in this case, finding such an equivalent fraction directly is challenging. This method is less practical for 15/16 but is useful for understanding the underlying principles.
Practical Applications of Decimal Equivalents
Understanding the decimal equivalent of fractions is crucial in various real-world applications:
- Measurement: Many measurements involve fractions (e.g., inches, centimeters). Converting these fractions to decimals simplifies calculations and comparisons.
- Finance: Calculations involving percentages, interest rates, and monetary values frequently use decimal representations.
- Engineering and Science: Precision in engineering and scientific calculations demands accurate decimal representations of fractions.
- Computer Programming: Many programming languages rely on decimal numbers for calculations and data representation.
Further Exploration: Recurring Decimals
While 15/16 conveniently converts to a terminating decimal (a decimal that ends), many fractions result in recurring decimals (decimals with repeating patterns). For example, 1/3 = 0.333... (the 3 repeats infinitely). Understanding the difference between terminating and recurring decimals is essential for working with fractions. The key difference lies in whether the denominator of the fraction, when simplified, contains prime factors other than 2 and 5. If it does, the decimal will recur. Since 16 = 2<sup>4</sup>, 15/16 will result in a terminating decimal.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: Can I convert any fraction to a decimal?
- A: Yes, any fraction can be converted to a decimal by dividing the numerator by the denominator. The result may be a terminating decimal or a recurring decimal.
-
Q: Is there a shortcut to convert fractions like 15/16 to decimals?
- A: While long division is fundamental, using a calculator is the most efficient method for practical applications.
-
Q: Why is it important to learn about converting fractions to decimals?
- A: This conversion is crucial for solving various mathematical problems in different fields, particularly those involving calculations and comparisons.
-
Q: What if I get a remainder after the long division?
- A: If you get a remainder after the long division, it means the fraction converts to a recurring decimal. You can either continue the long division until you identify the recurring pattern or round the decimal to a certain number of decimal places.
-
Q: How can I improve my skills in fraction to decimal conversions?
- A: Practice is key! Start with simpler fractions and gradually increase the complexity. Use both long division and a calculator to reinforce your understanding.
Conclusion
Converting 15/16 to its decimal equivalent, 0.9375, is a simple yet important skill in mathematics. We explored three methods – long division, calculator use, and a conceptual understanding of decimal place values – to achieve this conversion. Understanding these methods provides a solid foundation for working with fractions and decimals in various applications, from everyday calculations to complex scientific and engineering tasks. Remember, practice makes perfect! The more you practice converting fractions to decimals, the more confident and proficient you will become.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 15 16 As A Decimal . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.