17/9 As A Mixed Number
horsecheck
Sep 18, 2025 · 5 min read
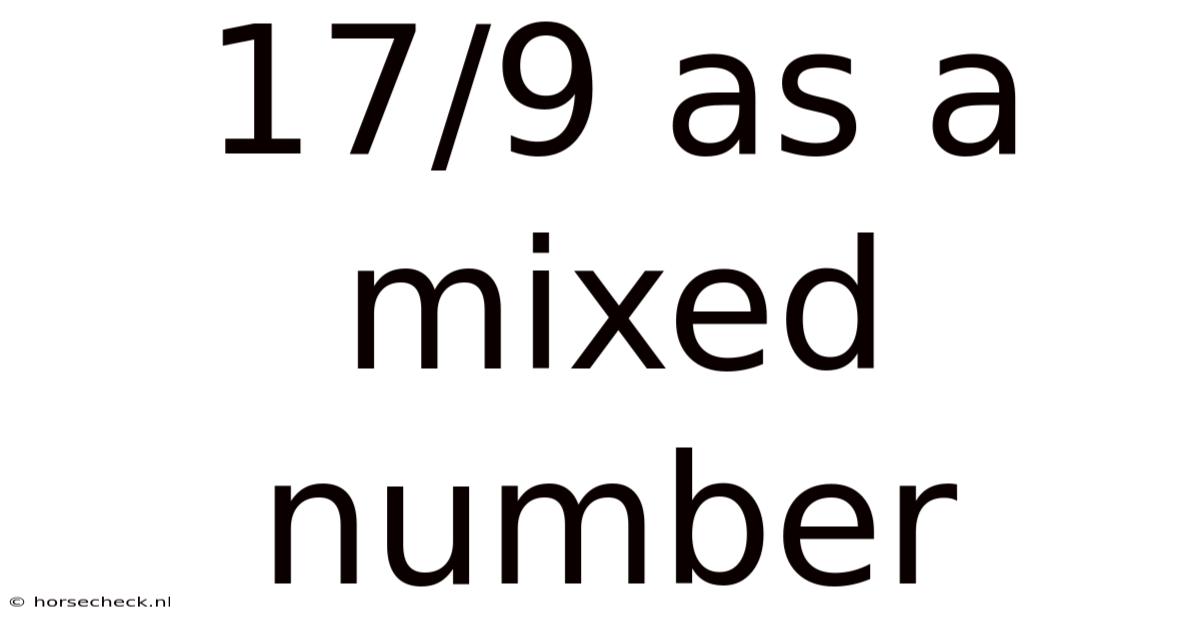
Table of Contents
Understanding 17/9 as a Mixed Number: A Comprehensive Guide
The fraction 17/9 represents a quantity greater than one whole. Understanding how to convert this improper fraction into a mixed number is a fundamental skill in mathematics, crucial for various applications from basic arithmetic to more advanced concepts. This comprehensive guide will not only show you how to convert 17/9 into a mixed number but also delve into the underlying principles, explore practical applications, and answer frequently asked questions. We'll break down the process step-by-step, making it easy to understand even for beginners.
What is a Mixed Number?
Before we dive into converting 17/9, let's clarify what a mixed number is. A mixed number combines a whole number and a proper fraction. A proper fraction is a fraction where the numerator (top number) is smaller than the denominator (bottom number), for example, 1/2, 2/3, or 5/8. Conversely, an improper fraction has a numerator larger than or equal to its denominator, like 7/4 or 17/9. Mixed numbers provide a more intuitive way to represent quantities larger than one whole. For instance, 1 1/2 is easier to visualize than 3/2.
Converting 17/9 to a Mixed Number: Step-by-Step
The conversion of 17/9 to a mixed number involves dividing the numerator by the denominator. Here's how:
Step 1: Perform the Division
Divide the numerator (17) by the denominator (9):
17 ÷ 9 = 1 with a remainder of 8
Step 2: Identify the Whole Number and the Remainder
From the division, we get:
- Quotient: 1 (this becomes the whole number part of our mixed number)
- Remainder: 8 (this becomes the numerator of the fractional part)
Step 3: Construct the Mixed Number
The denominator remains the same (9). Therefore, the mixed number representation of 17/9 is:
1 8/9
This means 17/9 represents one whole and eight-ninths of another whole.
Visualizing the Conversion
Imagine you have 17 identical pieces of pizza, and each pizza is divided into 9 equal slices. You can assemble 1 complete pizza (9 slices) and still have 8 slices left. Those 8 slices represent 8/9 of a second pizza. Hence, you have 1 whole pizza and 8/9 of another, perfectly illustrating 1 8/9.
The Importance of Understanding Mixed Numbers
The ability to convert between improper fractions and mixed numbers is crucial for several reasons:
- Simplifying Calculations: Mixed numbers often make calculations easier and more intuitive than working solely with improper fractions. Adding or subtracting mixed numbers can be simpler than working with their improper fraction equivalents.
- Real-World Applications: Mixed numbers are frequently encountered in everyday life, from measuring ingredients in cooking (1 1/2 cups of flour) to understanding distances (2 3/4 miles).
- Foundation for Advanced Mathematics: A solid grasp of mixed numbers is fundamental for understanding more advanced mathematical concepts, including algebra, geometry, and calculus.
Working with Mixed Numbers: Addition and Subtraction
Let's illustrate the practical use of mixed numbers with a simple example involving addition:
Suppose you need to add 1 8/9 and 2 1/9. Adding these as improper fractions would be more complex. Instead, you can directly add the whole numbers and the fractions separately:
1 + 2 = 3 (Whole number sum) 8/9 + 1/9 = 9/9 = 1 (Fractional sum)
Combining these, the result is 3 + 1 = 4.
Subtraction follows a similar pattern. However, you might need to borrow from the whole number if the fraction in the minuend (the number being subtracted from) is smaller than the fraction in the subtrahend (the number being subtracted). For example:
3 1/9 - 1 8/9
Since 1/9 is less than 8/9, we borrow 1 from the 3, converting it to 9/9 and adding it to 1/9:
(2 + 9/9 + 1/9) - 1 8/9 = 2 10/9 - 1 8/9 = 1 2/9
Converting Mixed Numbers back to Improper Fractions
The reverse process is also important. To convert a mixed number back into an improper fraction, follow these steps:
- Multiply the whole number by the denominator: For 1 8/9, this is 1 x 9 = 9
- Add the numerator to the result from step 1: 9 + 8 = 17
- Keep the same denominator: The denominator remains 9.
Therefore, 1 8/9 converts back to 17/9.
Beyond 17/9: Generalizing the Conversion Process
The method we used for 17/9 is applicable to any improper fraction. The key is always to divide the numerator by the denominator, expressing the result as a whole number and a remainder. The whole number becomes the whole number part of the mixed number, the remainder becomes the new numerator, and the denominator stays the same.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What if the remainder is zero?
A1: If the remainder is zero after dividing the numerator by the denominator, the improper fraction is actually a whole number. For example, 18/9 = 2 (because 18 ÷ 9 = 2 with no remainder).
Q2: Can I convert decimals to mixed numbers?
A2: Yes, you can. First, convert the decimal to a fraction, then convert the fraction to a mixed number if it's an improper fraction.
Q3: Are mixed numbers always the best way to represent quantities?
A3: Not necessarily. While mixed numbers are often more intuitive for everyday use, improper fractions can be more convenient in certain mathematical operations, particularly algebra. The choice depends on the context and the desired outcome.
Q4: How do I compare mixed numbers?
A4: To compare mixed numbers, first compare the whole number parts. If the whole numbers are different, the larger whole number corresponds to the larger mixed number. If the whole numbers are the same, compare the fractional parts.
Conclusion
Converting improper fractions like 17/9 to mixed numbers is a fundamental skill in mathematics. This process involves dividing the numerator by the denominator, identifying the quotient as the whole number and the remainder as the new numerator, while keeping the same denominator. Understanding this process, along with its practical applications and the ability to reverse the conversion, provides a strong foundation for further mathematical exploration and real-world problem-solving. Mastering this concept opens doors to more advanced mathematical concepts and enhances your ability to tackle a wide variety of mathematical problems with confidence and efficiency. Practice is key to solidifying your understanding, so don't hesitate to work through various examples to solidify your skills.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 17/9 As A Mixed Number . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.