19/9 As A Mixed Number
horsecheck
Sep 16, 2025 · 6 min read
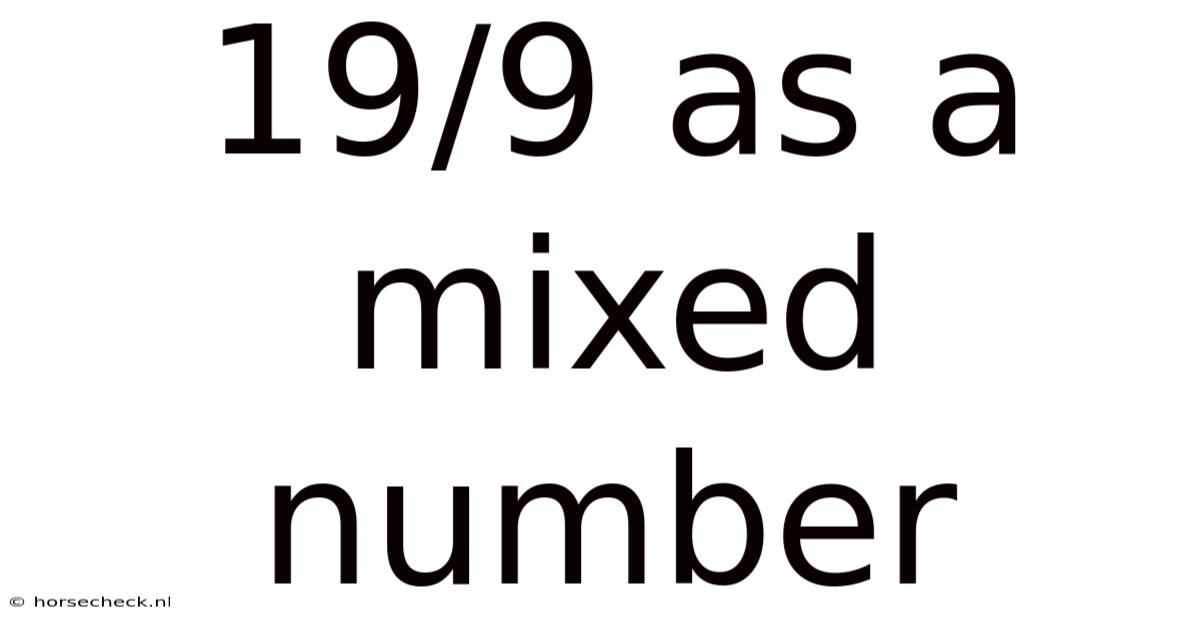
Table of Contents
Understanding 19/9 as a Mixed Number: A Comprehensive Guide
Fractions are fundamental building blocks in mathematics, forming the basis for more advanced concepts. Understanding how to convert improper fractions, like 19/9, into mixed numbers is crucial for various mathematical operations and applications. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of converting 19/9 into a mixed number, exploring the underlying concepts, providing step-by-step instructions, and answering frequently asked questions. We'll also look at the practical applications of this conversion and explore related mathematical ideas. Mastering this concept is a key step towards building a strong foundation in mathematics.
Introduction to Fractions and Mixed Numbers
Before we tackle 19/9, let's establish a clear understanding of fractions and mixed numbers. A fraction represents a part of a whole. It consists of a numerator (the top number) and a denominator (the bottom number). The numerator indicates how many parts we have, while the denominator indicates how many equal parts the whole is divided into. For example, in the fraction 3/4, the numerator is 3 and the denominator is 4, meaning we have 3 out of 4 equal parts.
An improper fraction is a fraction where the numerator is greater than or equal to the denominator. Examples include 7/4, 5/5, and, of course, our focus today, 19/9. Improper fractions represent a value greater than or equal to one.
A mixed number combines a whole number and a proper fraction. A proper fraction is a fraction where the numerator is smaller than the denominator (e.g., 1/2, 3/4). Mixed numbers provide a more intuitive way to represent quantities greater than one. For example, 1 3/4 represents one whole and three-quarters of another.
Converting 19/9 to a Mixed Number: A Step-by-Step Approach
Converting an improper fraction to a mixed number involves dividing the numerator by the denominator. The quotient becomes the whole number part of the mixed number, while the remainder becomes the numerator of the fractional part. The denominator remains the same. Let's apply this to 19/9:
Step 1: Divide the numerator by the denominator.
Divide 19 by 9. This gives us a quotient of 2 and a remainder of 1.
Step 2: Write the quotient as the whole number.
The quotient, 2, becomes the whole number part of our mixed number.
Step 3: Write the remainder as the numerator of the fraction.
The remainder, 1, becomes the numerator of the fractional part.
Step 4: Keep the original denominator.
The denominator remains 9.
Step 5: Combine the whole number and the fraction.
Combining the results from steps 2 and 3, we get the mixed number 2 1/9.
Therefore, 19/9 as a mixed number is 2 1/9.
Visual Representation: Understanding the Concept
Imagine you have 19 slices of pizza, and each pizza has 9 slices. You can make two full pizzas (18 slices) with one slice left over. This visually represents the conversion: 19 slices (numerator) divided into pizzas of 9 slices each (denominator) results in 2 whole pizzas and 1 remaining slice. This remaining slice represents the 1/9 fraction. This visual approach helps solidify the understanding of the conversion process.
Mathematical Explanation: The Division Algorithm
The conversion process is rooted in the division algorithm, a fundamental concept in arithmetic. The division algorithm states that for any integers a (dividend) and b (divisor), where b is not zero, there exist unique integers q (quotient) and r (remainder) such that:
a = b q + r, where 0 ≤ r < b
In our case, a = 19, b = 9. When we divide 19 by 9, we get q = 2 and r = 1. This directly translates to the mixed number representation: 2 (whole number) and 1/9 (fractional part).
Applications of Converting Improper Fractions to Mixed Numbers
Converting improper fractions to mixed numbers is essential in various mathematical contexts and real-world applications:
-
Measurement: When dealing with measurements involving fractions of units (e.g., inches, feet, meters), mixed numbers provide a more practical and understandable representation. For example, expressing a length of 19/9 meters as 2 1/9 meters is clearer and easier to grasp.
-
Baking and Cooking: Recipes often require fractions of ingredients. Converting improper fractions to mixed numbers makes measuring ingredients more efficient and less prone to error.
-
Construction and Engineering: In construction and engineering, precise measurements are crucial. Converting fractions to mixed numbers enhances clarity and accuracy in blueprints and calculations.
-
Everyday Life: Numerous situations require understanding and utilizing fractions. Sharing items, calculating proportions, or understanding data representation often involve converting between improper fractions and mixed numbers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Can all improper fractions be converted into mixed numbers?
A: Yes, all improper fractions can be converted into mixed numbers. This is a direct consequence of the division algorithm.
Q2: What if the remainder is zero after dividing the numerator by the denominator?
A: If the remainder is zero, it means the improper fraction is a whole number. For example, 18/9 = 2. There's no fractional part in the mixed number representation.
Q3: Is there more than one way to represent a mixed number?
A: No, there is only one way to represent a mixed number in its simplest form. The fractional part should be simplified to its lowest terms. For example, 2 2/4 should be simplified to 2 1/2.
Q4: How can I convert a mixed number back into an improper fraction?
A: To convert a mixed number back to an improper fraction, multiply the whole number by the denominator, add the numerator, and place the result over the original denominator. For example, to convert 2 1/9 back to an improper fraction: (2 * 9) + 1 = 19, so the improper fraction is 19/9.
Q5: Why is understanding this conversion important for further mathematical studies?
A: This seemingly simple conversion is a cornerstone for more advanced mathematical concepts. It's crucial for operations with fractions, solving equations, working with algebraic expressions, and progressing to topics like decimals, percentages, and ratios. A solid understanding ensures a smoother transition to these higher-level mathematical concepts.
Conclusion: Mastering the Conversion of 19/9
Converting the improper fraction 19/9 to the mixed number 2 1/9 is a fundamental skill in mathematics. Understanding the process, whether through the step-by-step approach, the visual representation, or the mathematical explanation based on the division algorithm, builds a strong foundation for further mathematical learning. The ability to easily switch between improper fractions and mixed numbers enhances comprehension and proficiency in various mathematical contexts and real-world applications. This seemingly small concept plays a significant role in more complex mathematical tasks, ultimately shaping your overall understanding of numbers and their relationships. Remember to practice regularly to solidify your understanding and improve your problem-solving skills. The journey to mastering mathematics is a rewarding one, and this conversion forms an essential stepping stone along the way.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 19/9 As A Mixed Number . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.