2 3 Multiplied By 2
horsecheck
Sep 22, 2025 · 6 min read
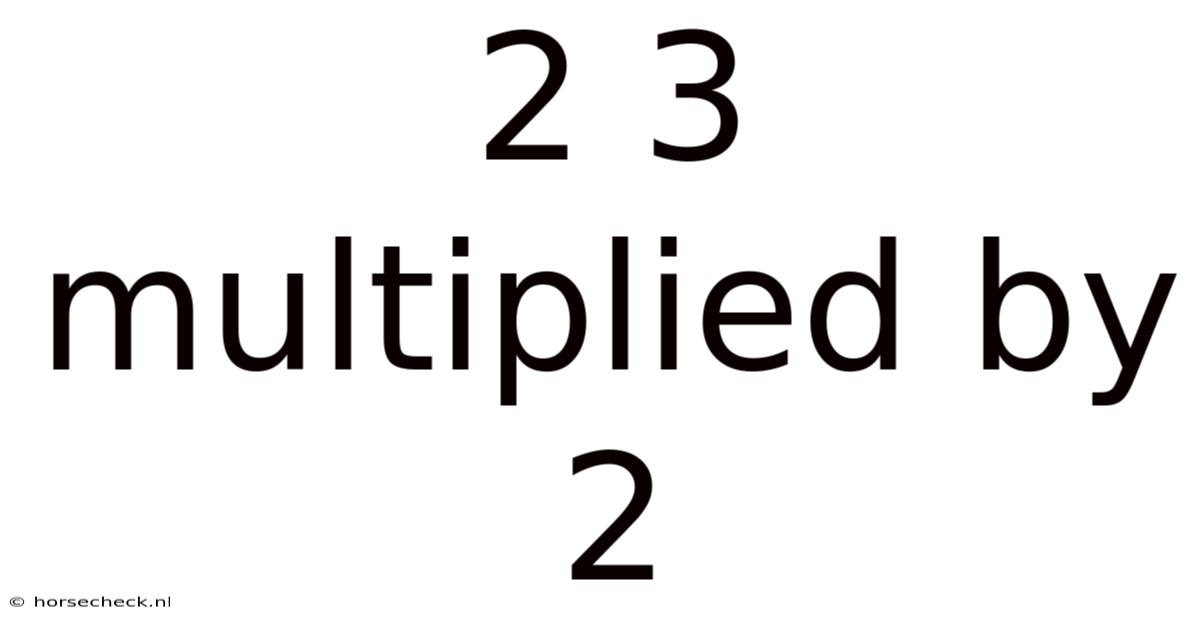
Table of Contents
Unpacking the Simple Yet Profound: 2 x 3 x 2
This article delves into the seemingly straightforward mathematical problem of 2 multiplied by 3 multiplied by 2 (2 x 3 x 2 = ?), expanding beyond the simple answer to explore the underlying concepts, different approaches to solving it, and its broader implications in mathematics and beyond. Understanding this seemingly basic calculation forms a foundational block for more complex mathematical operations. This exploration will be accessible to all levels, from elementary school students to those seeking a deeper understanding of mathematical principles.
Introduction: More Than Just a Number
The calculation 2 x 3 x 2 might seem trivial, a problem easily solved by even young children. However, beneath its simplicity lies a wealth of mathematical concepts that are crucial for understanding more complex arithmetic, algebra, and even higher-level mathematics. This article unpacks these concepts, showing how this simple equation exemplifies core principles of multiplication and order of operations. We will explore different methods for solving this problem, highlighting the flexibility and power of mathematics.
Understanding Multiplication: The Foundation
At its core, multiplication is repeated addition. When we say 2 x 3, we're essentially adding two, three times: 2 + 2 + 2 = 6. Similarly, 3 x 2 means adding three, two times: 3 + 3 = 6. This repeated addition concept is fundamental to understanding how multiplication works, and it's particularly helpful when visualizing the process, especially for younger learners. The problem 2 x 3 x 2 can be broken down using this principle in several ways, which we'll explore in the following sections.
Methods for Solving 2 x 3 x 2
There are several ways to approach this seemingly simple multiplication problem. The choice of method often depends on personal preference, the level of mathematical understanding, and the context of the problem.
Method 1: Sequential Multiplication
This is the most straightforward approach. We simply perform the multiplications one after the other, from left to right:
- 2 x 3 = 6
- 6 x 2 = 12
Therefore, 2 x 3 x 2 = 12. This method highlights the associative property of multiplication, which states that the order in which we group the numbers doesn't change the result.
Method 2: Commutative Property
The commutative property of multiplication states that the order of the numbers being multiplied doesn't affect the product. This means we can rearrange the numbers:
2 x 3 x 2 = 2 x 2 x 3
- 2 x 2 = 4
- 4 x 3 = 12
This method demonstrates the flexibility offered by the commutative property, allowing us to choose the order that's easiest to calculate. For instance, multiplying 2 x 2 is often simpler than 2 x 3 for many individuals.
Method 3: Using Arrays or Visual Models
Visual aids can be particularly helpful for younger learners or those who benefit from a more concrete representation of mathematical concepts. We can represent 2 x 3 x 2 using an array:
Imagine two rows of three objects each. This represents 2 x 3 = 6. Now, imagine we have two such sets of these rows. This is where the second '2' comes in. Therefore, we end up with a total of 12 objects. This method provides a visual understanding of the concept of repeated multiplication. Think of it like stacking rectangular boxes, or arranging items on shelves.
Method 4: The Distributive Property
While less intuitive for this specific problem, the distributive property (a(b + c) = ab + ac) can be applied in more complex scenarios involving multiplication. It highlights the connection between multiplication and addition. However, its direct application to 2 x 3 x 2 isn't as clear-cut as the previous methods.
The Importance of Order of Operations (PEMDAS/BODMAS)
While the commutative property allows us to rearrange the numbers in this specific problem, this isn't always the case. When dealing with more complex equations involving addition, subtraction, division, and exponents, the order of operations becomes crucial. The acronym PEMDAS (Parentheses, Exponents, Multiplication and Division, Addition and Subtraction) or BODMAS (Brackets, Orders, Division and Multiplication, Addition and Subtraction) guides us through the correct sequence.
In this case, because we only have multiplication, the order doesn't matter. However, understanding PEMDAS/BODMAS is essential for tackling more challenging mathematical problems.
Real-World Applications
While seemingly simple, the principle of multiplication, as exemplified by 2 x 3 x 2, is fundamental to numerous real-world applications:
- Calculating Costs: If apples cost $2 each, and you buy 3 bags with 2 apples each, the total cost is 2 x 3 x 2 = $12.
- Measuring Area: Imagine a rectangular room that's 2 meters wide and 3 meters long. If you have two such rooms, the total area is 2 x 3 x 2 = 12 square meters.
- Counting Objects: If you have 2 boxes, each containing 3 bags, and each bag holds 2 marbles, you have a total of 2 x 3 x 2 = 12 marbles.
These examples demonstrate how the basic principle of multiplication underlies countless everyday calculations.
Expanding the Concept: Beyond 2 x 3 x 2
The simple equation 2 x 3 x 2 serves as a springboard for understanding more complex mathematical concepts:
- Algebra: The principles learned here can be extended to algebraic expressions, where variables replace numbers.
- Geometry: Calculating volumes and areas often involves multiple multiplications, building upon the foundation established by simple equations like this one.
- Calculus: Higher-level mathematics heavily relies on an understanding of basic arithmetic operations.
Therefore, mastering this seemingly simple problem is a crucial step toward more advanced mathematical skills.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Is there only one correct answer to 2 x 3 x 2?
A: Yes, there is only one correct answer: 12. While different methods can be used to arrive at the answer, the result remains constant due to the associative and commutative properties of multiplication.
Q: Why is understanding the order of operations important?
A: The order of operations ensures consistency and accuracy in calculations, particularly in more complex equations involving multiple operations. Without a defined order, different interpretations could lead to vastly different results.
Q: How can I help my child understand multiplication?
A: Use visual aids like counters, blocks, or drawings to represent the multiplication. Break down problems into smaller, manageable steps, and relate multiplication to real-world situations. Games and interactive activities can also make learning more engaging.
Q: What if the numbers were different? How would the process change?
A: The process remains the same, regardless of the numbers involved. We would simply apply the same principles of multiplication and, if necessary, the order of operations, to arrive at the correct answer.
Q: Can this simple equation be used to explain more advanced mathematical concepts?
A: Absolutely! It's a building block for understanding concepts like the distributive property, associative property, commutative property, and eventually, more advanced topics in algebra, geometry, and calculus.
Conclusion: The Power of Simplicity
The seemingly simple calculation 2 x 3 x 2 offers a surprisingly rich learning experience. It showcases fundamental mathematical concepts, highlights different solution methods, and underscores the importance of order of operations. Understanding this seemingly trivial problem is not just about arriving at the answer (12); it's about grasping the underlying principles that form the foundation for more advanced mathematical understanding. By exploring this problem thoroughly, we appreciate the power and elegance of even the simplest mathematical operations, building a strong foundation for future learning and problem-solving. The journey from a simple calculation to a deeper understanding of mathematical principles is a testament to the inherent beauty and power of mathematics.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Lcm For 10 And 12
Sep 23, 2025
-
What Is A 20 22 Grade
Sep 23, 2025
-
Roman Numerals Multiplying To 35
Sep 23, 2025
-
15 16 On A Tape Measure
Sep 23, 2025
-
What Percent Is 13 15
Sep 23, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 2 3 Multiplied By 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.