20 Divided By 5 2
horsecheck
Sep 23, 2025 · 5 min read
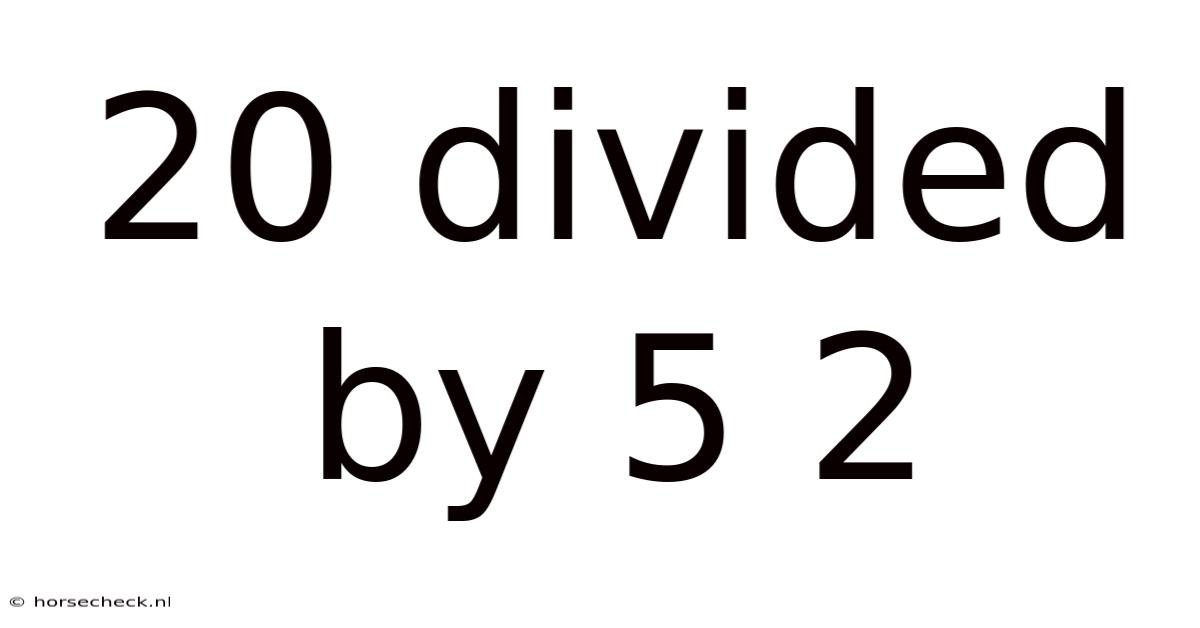
Table of Contents
Decoding 20 Divided by 5: A Deep Dive into Mathematical Operations
This article will thoroughly explore the seemingly simple mathematical problem: 20 divided by 5. While the answer might seem instantly obvious to many, we'll delve into the underlying principles, exploring different methods of solving the problem, its application in real-world scenarios, and address common misconceptions. Understanding this seemingly basic calculation is fundamental to grasping more complex mathematical concepts. We'll also discuss the importance of order of operations and how this impacts the interpretation and solution of similar problems.
Understanding Division: The Basics
Division is one of the four fundamental arithmetic operations, alongside addition, subtraction, and multiplication. It represents the process of splitting a quantity into equal parts or groups. In the expression "20 divided by 5," we are essentially asking: "How many times does 5 go into 20?" or "If we divide 20 into 5 equal groups, how many are in each group?"
The components of a division problem are:
- Dividend: The number being divided (in this case, 20).
- Divisor: The number we are dividing by (in this case, 5).
- Quotient: The result of the division (the answer).
- Remainder: The amount left over if the division doesn't result in a whole number.
Methods for Solving 20 Divided by 5
There are several ways to approach this problem, each offering a different perspective on the underlying concept of division.
1. Repeated Subtraction:
This method involves repeatedly subtracting the divisor (5) from the dividend (20) until we reach zero. The number of times we subtract represents the quotient.
20 - 5 = 15 15 - 5 = 10 10 - 5 = 5 5 - 5 = 0
We subtracted 5 four times, therefore, 20 divided by 5 equals 4.
2. Multiplication as the Inverse Operation:
Division and multiplication are inverse operations. This means that if we multiply the quotient by the divisor, we should get the dividend. We can think, "What number multiplied by 5 equals 20?" The answer is 4 (4 x 5 = 20). Therefore, 20 divided by 5 is 4.
3. Using a Division Algorithm (Long Division):
While seemingly unnecessary for such a simple problem, long division provides a structured approach that becomes invaluable for more complex divisions.
4
5 | 20
-20
--
0
This shows that 5 goes into 20 four times with no remainder.
4. Visual Representation:
We can visualize this problem by imagining 20 objects (e.g., apples) and dividing them into 5 equal groups. Each group would contain 4 apples.
Real-World Applications of Division
Understanding division is crucial for countless real-world applications, from everyday tasks to complex scientific calculations. Here are just a few examples:
- Sharing equally: Dividing a pizza among friends, sharing candy among siblings, or splitting a bill at a restaurant all involve division.
- Calculating rates and ratios: Determining speed (distance divided by time), unit price (total cost divided by quantity), or fuel efficiency (miles driven divided by gallons of gas) all rely on division.
- Scaling recipes: If a recipe calls for ingredients for 4 servings and you want to make it for 8, you'll need to multiply the quantities by 2 (or divide the original quantities by 0.5).
- Financial calculations: Dividing total expenses by the number of months gives the average monthly expense.
- Averaging values: Calculating the average test score, average rainfall, or average temperature all involve division.
Expanding the Concept: Addressing the "2" in the Original Query
The original question, "20 divided by 5 2," is ambiguous unless we clarify the meaning of "5 2". If it represents a combined operation or a typographical error, the solution changes significantly.
Scenario 1: "20 divided by (5 x 2)"
This interpretation introduces the concept of order of operations, often remembered by the acronym PEMDAS (Parentheses, Exponents, Multiplication and Division, Addition and Subtraction). We must perform the multiplication within the parentheses first:
(5 x 2) = 10
Then, we divide 20 by 10:
20 / 10 = 2
In this scenario, the answer is 2.
Scenario 2: "20 divided by 5, then multiplied by 2"
If "5 2" implies a multiplication immediately following the division, then the order of operations dictates we perform the division first, and then the multiplication:
20 / 5 = 4 4 x 2 = 8
In this case, the answer is 8.
Scenario 3: Typographical Error
It's possible "5 2" is simply a typographical error. If it's meant to be "52", then the question would be fundamentally different, requiring a long division calculation:
20 / 52 = 0.3846... (approximately)
Addressing Common Misconceptions
Several common misconceptions can arise when dealing with division:
- Confusing the dividend and the divisor: Students sometimes mistakenly divide the smaller number by the larger number. It's important to understand which number is being divided (the dividend) and which number we are dividing by (the divisor).
- Ignoring remainders: When dividing whole numbers, sometimes there's a remainder. It's essential to understand how to express the answer, either as a whole number with a remainder or as a decimal or fraction.
- Order of Operations Errors: As seen in Scenario 1, neglecting the correct order of operations leads to incorrect answers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: What is the inverse operation of division?
- A: Multiplication.
-
Q: What happens when you divide by zero?
- A: Division by zero is undefined in mathematics.
-
Q: How do I divide larger numbers?
- A: For larger numbers, the long division method or a calculator becomes more efficient.
-
Q: Can you have a negative quotient?
- A: Yes, if either the dividend or the divisor (but not both) is negative.
-
Q: How do I handle remainders?
- A: You can express the remainder as a separate value (e.g., "5 with a remainder of 2") or convert it into a decimal or fraction.
Conclusion
The seemingly simple operation of 20 divided by 5 provides a gateway to a deeper understanding of division, its applications, and related mathematical concepts. By exploring different solution methods and emphasizing the importance of order of operations, we can build a strong foundation for tackling more complex mathematical problems. Remember, the key is not just to get the answer but to understand the process and the underlying principles involved. This foundation allows for greater confidence and success in tackling more advanced mathematics. The seemingly simple act of dividing 20 by 5 is far richer and more significant than it first appears, touching upon core principles crucial for success in numerous fields.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 30 Off 55
Sep 23, 2025
-
Convert 7 10 To Percentage
Sep 23, 2025
-
What Is 15 Of 26
Sep 23, 2025
-
What Is A 28 32 Grade
Sep 23, 2025
-
7 Percent As A Fraction
Sep 23, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 20 Divided By 5 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.