27/16 As A Mixed Number
horsecheck
Sep 17, 2025 · 5 min read
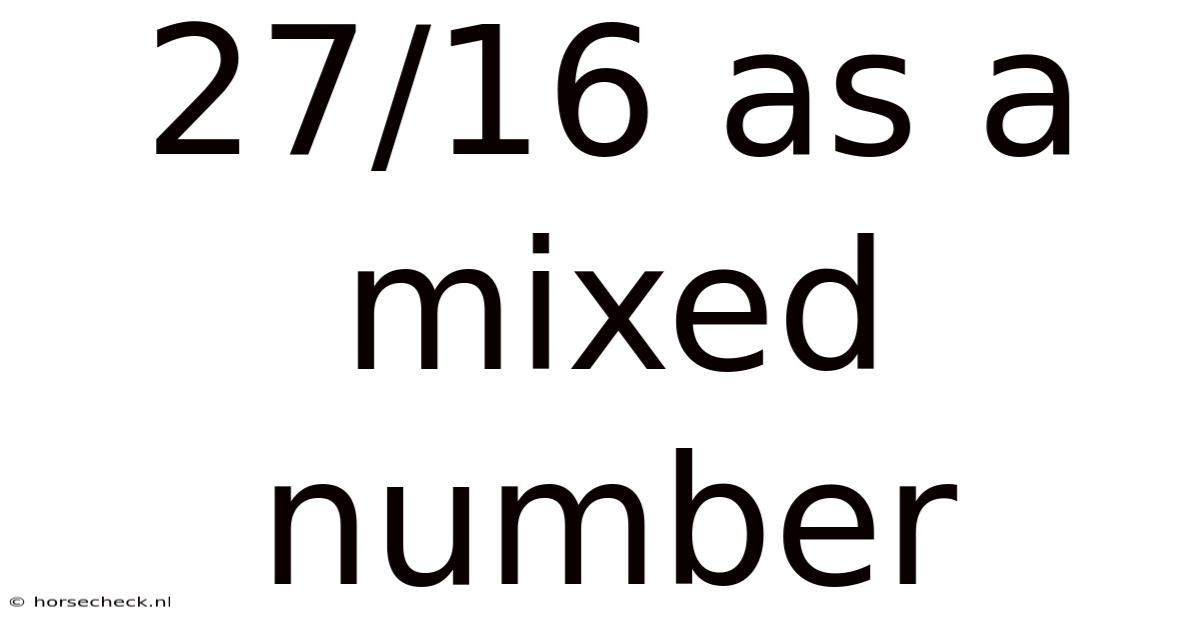
Table of Contents
Understanding 27/16 as a Mixed Number: A Comprehensive Guide
Converting improper fractions, like 27/16, into mixed numbers is a fundamental skill in arithmetic. This comprehensive guide will not only show you how to convert 27/16 into a mixed number but also delve deeper into the underlying concepts, providing a solid foundation for understanding fractions. We'll explore different methods, tackle related concepts, and answer frequently asked questions to ensure a thorough understanding. This guide aims to provide you with the tools and knowledge to confidently tackle similar fraction conversions in the future.
What is a Mixed Number?
Before we dive into converting 27/16, let's define what a mixed number is. A mixed number combines a whole number and a proper fraction. A proper fraction is a fraction where the numerator (the top number) is smaller than the denominator (the bottom number). For example, 1 ¾ is a mixed number; 1 is the whole number, and ¾ is the proper fraction. Understanding this distinction is crucial for grasping the conversion process.
Converting 27/16 to a Mixed Number: The Method
The improper fraction 27/16 means we have 27 parts of a whole that's divided into 16 equal parts. Since 16 parts make a whole, we can determine how many whole numbers are contained within 27/16. This is done through division.
Step 1: Divide the Numerator by the Denominator
Divide the numerator (27) by the denominator (16):
27 ÷ 16 = 1 with a remainder of 11
Step 2: Identify the Whole Number and the Remainder
The quotient (the result of the division) becomes the whole number part of your mixed number. In this case, the quotient is 1. The remainder (the amount left over after the division) becomes the numerator of the proper fraction. Here, the remainder is 11.
Step 3: Form the Mixed Number
The denominator of the proper fraction remains the same as the original denominator (16). Therefore, combining the whole number and the fraction, we get:
1 ¹¹⁄₁₆
Therefore, 27/16 as a mixed number is 1 ¹¹⁄₁₆.
Visualizing the Conversion
Imagine you have 27 pizzas sliced into 16 pieces each. You can assemble 1 complete pizza using 16 slices. You'll have 11 slices left over. This visually represents the mixed number 1 ¹¹⁄₁₆. Each whole pizza represents the whole number 1, and the remaining 11 slices out of 16 represent the fraction ¹¹⁄₁₆.
Understanding Improper Fractions
An improper fraction is a fraction where the numerator is greater than or equal to the denominator. These fractions represent values greater than or equal to one. 27/16 is an improper fraction because 27 (the numerator) is greater than 16 (the denominator). Converting improper fractions to mixed numbers makes it easier to visualize and understand their magnitude.
Converting Mixed Numbers Back to Improper Fractions
It's equally important to understand the reverse process – converting a mixed number back into an improper fraction. This skill is often needed in more complex mathematical operations. Let's use our example, 1 ¹¹⁄₁₆:
Step 1: Multiply the whole number by the denominator
Multiply the whole number (1) by the denominator (16): 1 x 16 = 16
Step 2: Add the numerator
Add the result from Step 1 to the numerator (11): 16 + 11 = 27
Step 3: Place the result over the original denominator
Place the sum from Step 2 over the original denominator (16): 27/16
This confirms that we've correctly converted 27/16 to 1 ¹¹⁄₁₆ and back again. This reversibility is a key aspect of understanding fraction conversions.
Applications of Mixed Numbers
Mixed numbers are frequently used in everyday life and various fields, including:
- Cooking: Recipes often call for mixed numbers of cups or teaspoons of ingredients (e.g., 2 ½ cups of flour).
- Measurement: Measuring lengths, weights, and volumes frequently involves mixed numbers (e.g., 5 ¾ inches).
- Construction: Blueprints and construction plans often use mixed numbers for precise dimensions.
- Time: Telling time involves mixed numbers (e.g., 2:45 which can be represented as 2 ¾ hours past 2:00).
Beyond 27/16: Practicing Fraction Conversions
Mastering the conversion of improper fractions to mixed numbers requires practice. Try converting these improper fractions to mixed numbers:
- 35/8
- 47/12
- 61/9
- 100/7
Remember the steps: divide the numerator by the denominator, use the quotient as the whole number, and use the remainder as the new numerator, keeping the original denominator.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What if the remainder is zero?
A: If the remainder is zero after dividing the numerator by the denominator, it means the improper fraction is already a whole number. For instance, 16/16 = 1.
Q: Can I use a calculator for these conversions?
A: While calculators can perform the division, understanding the underlying process is crucial for developing a strong mathematical foundation. Calculators are helpful for checking your work, but you should strive to perform the conversions manually.
Q: Why are mixed numbers important?
A: Mixed numbers provide a more intuitive way to represent quantities that are greater than one. They are easier to visualize and use in practical applications than improper fractions.
Q: Are there other ways to represent 27/16?
A: While 1 ¹¹⁄₁₆ is the standard mixed number representation, you could also express it as a decimal (1.6875). However, mixed numbers are preferred in many contexts because they maintain the fractional representation of the remainder.
Conclusion
Converting improper fractions like 27/16 to mixed numbers is a fundamental skill with wide-ranging applications. By understanding the process of division, identifying the whole number and remainder, and forming the mixed number, you can confidently tackle similar conversions. Remember to practice to solidify your understanding and build a solid foundation in fractional arithmetic. The ability to seamlessly convert between improper fractions and mixed numbers is crucial for success in various mathematical and real-world applications. The steps outlined here, combined with regular practice, will ensure you master this important skill. Continue practicing, and you'll find that fraction conversions become second nature.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 27/16 As A Mixed Number . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.