27/2 As A Mixed Number
horsecheck
Sep 18, 2025 · 5 min read
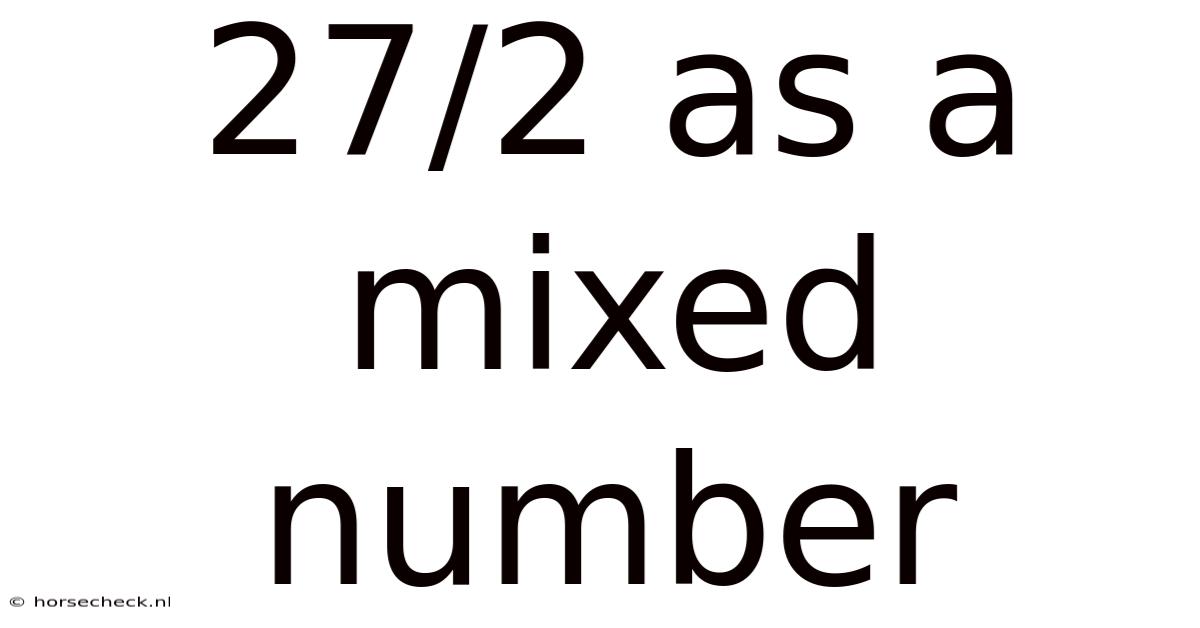
Table of Contents
Understanding 27/2 as a Mixed Number: A Comprehensive Guide
The fraction 27/2, also known as twenty-seven halves, represents a value greater than one. Understanding how to convert this improper fraction into a mixed number is a fundamental skill in arithmetic. This comprehensive guide will not only show you how to perform this conversion but also delve deeper into the underlying concepts, providing you with a thorough understanding of fractions and mixed numbers. We'll explore different methods, address common questions, and provide practice examples to solidify your grasp of this important mathematical concept. By the end, you'll be confident in converting any improper fraction into its mixed number equivalent.
What is a Mixed Number?
Before we tackle 27/2 specifically, let's clarify the definition of a mixed number. A mixed number combines a whole number and a proper fraction. A proper fraction is a fraction where the numerator (the top number) is smaller than the denominator (the bottom number). For example, 1 ½, 3 ¼, and 5 ⅔ are all mixed numbers. They represent a quantity that's more than one whole unit but less than the next whole number.
Converting an Improper Fraction to a Mixed Number
An improper fraction is a fraction where the numerator is greater than or equal to the denominator. 27/2 is an improper fraction because 27 (the numerator) is larger than 2 (the denominator). To convert an improper fraction to a mixed number, we need to determine how many whole numbers are contained within the fraction and what fraction remains. There are two primary methods to achieve this:
Method 1: Division
This is the most straightforward method. We simply divide the numerator by the denominator.
-
Divide: Divide 27 by 2. 27 ÷ 2 = 13 with a remainder of 1.
-
Whole Number: The quotient (the result of the division) becomes the whole number part of the mixed number. In this case, the whole number is 13.
-
Fraction: The remainder becomes the numerator of the fraction, and the original denominator remains the same. The remainder is 1, so the fraction is 1/2.
-
Mixed Number: Combine the whole number and the fraction to form the mixed number. Therefore, 27/2 = 13 ½.
Method 2: Repeated Subtraction
This method is more conceptually illustrative, especially for beginners. We repeatedly subtract the denominator from the numerator until we reach a value less than the denominator.
-
Subtract: Subtract the denominator (2) from the numerator (27) repeatedly:
- 27 - 2 = 25
- 25 - 2 = 23
- 23 - 2 = 21
- 21 - 2 = 19
- 19 - 2 = 17
- 17 - 2 = 15
- 15 - 2 = 13
- 13 - 2 = 11
- 11 - 2 = 9
- 9 - 2 = 7
- 7 - 2 = 5
- 5 - 2 = 3
- 3 - 2 = 1
-
Count Subtractions: We subtracted 2 from 27 thirteen times. This represents the whole number part of our mixed number (13).
-
Remainder: The final result of the subtractions is 1. This is the remainder, which becomes the numerator of the fraction. The denominator remains 2.
-
Mixed Number: Combining the whole number and the fraction, we get 13 ½.
Visual Representation
Imagine you have 27 equally sized pieces of pizza. If you want to divide them into groups of 2, how many full groups will you have, and how many pieces will be left over? You'll have 13 full groups (13 x 2 = 26) with 1 piece remaining. This visually demonstrates that 27/2 is equal to 13 ½.
Converting a Mixed Number back to an Improper Fraction
It's equally important to understand the reverse process. To convert a mixed number (like 13 ½) back to an improper fraction:
-
Multiply: Multiply the whole number by the denominator: 13 x 2 = 26.
-
Add: Add the result to the numerator of the fraction: 26 + 1 = 27.
-
Improper Fraction: This sum becomes the new numerator, while the denominator remains the same. Therefore, 13 ½ = 27/2.
Practical Applications of Mixed Numbers
Mixed numbers are widely used in various real-world scenarios:
-
Measurement: Measuring lengths, weights, and volumes often involves mixed numbers (e.g., 2 ½ feet, 5 ¾ pounds).
-
Cooking: Recipes frequently use mixed numbers to specify ingredient quantities (e.g., 1 ¼ cups of flour).
-
Construction: Blueprints and construction plans use mixed numbers to represent dimensions.
Why is Understanding Mixed Numbers Important?
Mastering the conversion between improper fractions and mixed numbers is crucial for several reasons:
-
Simplification: Mixed numbers are often easier to visualize and understand than improper fractions.
-
Problem Solving: Many mathematical problems require converting between these two forms for efficient calculation.
-
Real-world Applications: As mentioned above, mixed numbers are essential in many practical contexts.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Can all improper fractions be converted to mixed numbers?
A: Yes, any improper fraction can be converted to a mixed number. If the numerator is exactly divisible by the denominator, the resulting mixed number will have a zero as the fractional part (e.g., 8/2 = 4).
Q: Is there a difference between 27/2 and 13 ½?
A: No, they represent the same quantity. They are simply different ways of expressing the same value.
Q: What if I have a larger improper fraction, like 100/7?
A: The same principles apply. Divide 100 by 7 (14 with a remainder of 2) to get the mixed number 14 ⅔.
Q: Can I use a calculator to convert improper fractions to mixed numbers?
A: Many calculators have this functionality. However, understanding the manual process is crucial for a deeper understanding of the concepts involved.
Conclusion
Converting 27/2 to a mixed number, resulting in 13 ½, is a fundamental skill in mathematics. This process, whether through division or repeated subtraction, is straightforward. Understanding the underlying concepts of proper fractions, improper fractions, and mixed numbers is essential for success in various mathematical applications and real-world scenarios. Practice is key to mastering these conversions and building a strong foundation in arithmetic. Remember the steps, visualize the process, and soon you’ll be confidently converting fractions with ease. Don't hesitate to practice with different improper fractions to solidify your understanding and build your mathematical confidence.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 27/2 As A Mixed Number . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.