3 16 Vs 5 16
horsecheck
Sep 24, 2025 · 6 min read
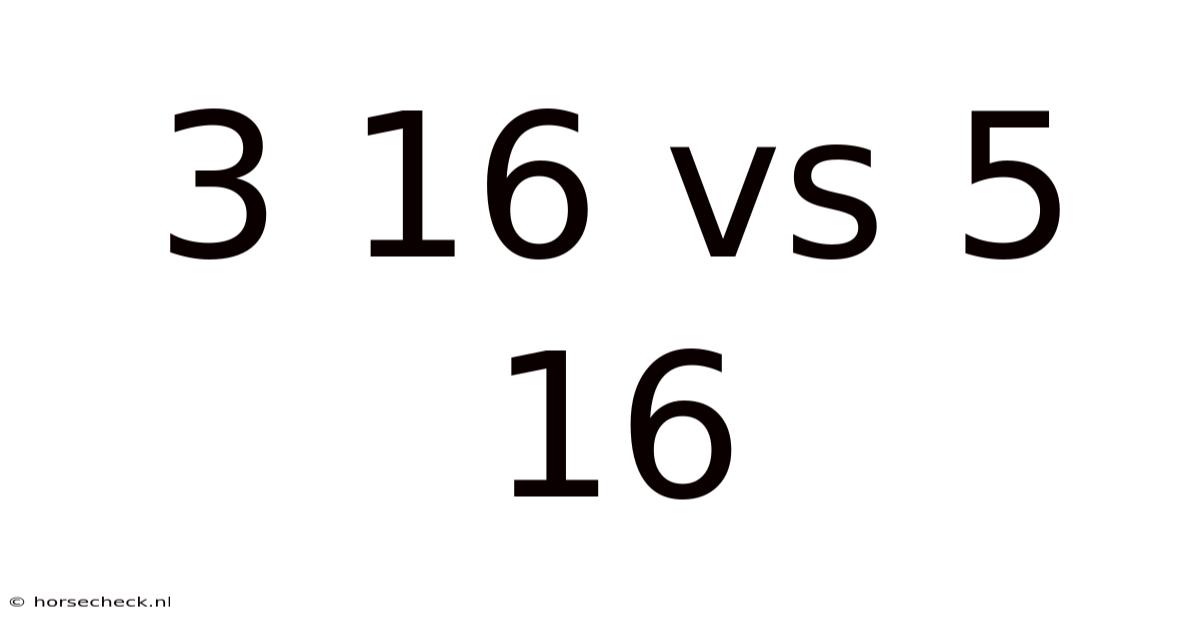
Table of Contents
Decoding the Difference: 3/16" vs 5/16" - A Deep Dive into Fractional Inches
Understanding fractional inches is crucial in various fields, from woodworking and mechanics to engineering and construction. This detailed guide will explore the differences between 3/16" and 5/16", two commonly encountered fractional measurements. We’ll delve into their numerical values, practical applications, and the implications of choosing one over the other in different contexts. This comprehensive comparison will equip you with the knowledge to confidently work with these measurements.
Understanding Fractional Inches
Before diving into the specifics of 3/16" and 5/16", let's establish a firm grasp of fractional inches. Fractional inches represent parts of an inch, using a numerator (top number) and a denominator (bottom number) to express the fraction. The denominator indicates how many equal parts the inch is divided into, while the numerator shows how many of those parts are being considered. For example, 1/2 inch means the inch is divided into two equal parts, and we are considering one of those parts.
Numerical Comparison: 3/16" vs 5/16"
The core difference between 3/16" and 5/16" lies in their numerical values. Let's break it down:
-
3/16 inch: This represents three out of sixteen equal parts of an inch. It's a smaller fraction compared to 5/16".
-
5/16 inch: This represents five out of sixteen equal parts of an inch. It's larger than 3/16", representing two more sixteenths of an inch.
To visualize this difference, imagine dividing an inch into 16 equal segments. 3/16" would occupy three of these segments, while 5/16" would occupy five. This difference, seemingly small, can have significant consequences depending on the application.
Decimal Equivalents and Conversions
For easier comparison and calculations, it's helpful to convert these fractions into decimal equivalents:
-
3/16 inch ≈ 0.1875 inches
-
5/16 inch ≈ 0.3125 inches
The decimal equivalents highlight the numerical gap between the two measurements more clearly: 0.3125 inches is approximately 0.125 inches (or 1/8 inch) larger than 0.1875 inches. This difference is crucial in precision work where even small discrepancies can lead to significant errors.
Practical Applications and Choosing the Right Measurement
The choice between 3/16" and 5/16" depends entirely on the specific application. Let's consider some examples:
Woodworking:
-
3/16" drill bit: Used for smaller holes, perhaps for dowels or pilot holes for screws in thinner materials. Using a larger bit could result in an oversized hole, compromising the structural integrity of the wood.
-
5/16" drill bit: Used for larger holes, possibly for larger screws, bolts, or through-holes in thicker materials. A smaller bit would be inadequate for these applications.
Similarly, when choosing screws, 3/16" screws are smaller and suitable for lighter duty applications, while 5/16" screws offer greater strength and holding power for heavier applications.
Mechanics and Engineering:
-
3/16" bolts and nuts: Often found in smaller assemblies or where less clamping force is required.
-
5/16" bolts and nuts: Commonly used in applications demanding higher tensile strength and clamping force, often found in heavier machinery or structural components.
The selection of the correct size bolt or nut is critical for the safety and functionality of any mechanical system. Using an incorrectly sized fastener could lead to failure, resulting in damage or injury.
Other Applications:
These measurements also find applications in plumbing, electrical work, and various other trades. The precise dimension is critical for the correct fit and function of components. Inaccurate measurements could result in leaks, shorts, or other malfunctions.
Visualizing the Difference: A Practical Example
Let's consider a practical example to further illustrate the difference:
Imagine you're building a wooden frame. You need to drill holes for dowels to join the pieces. If you use a 3/16" drill bit, the dowels will fit snugly but may not offer maximum strength. If you use a 5/16" drill bit, the dowels may have too much play, resulting in a weaker joint and instability in the frame.
This example demonstrates that selecting the correct measurement is vital for achieving the desired result. The seemingly small difference between 3/16" and 5/16" can drastically impact the final outcome, highlighting the importance of precision in measurement.
Understanding Tolerances
In engineering and manufacturing, the concept of tolerance is crucial. Tolerance defines the acceptable range of variation from a specified measurement. A part may be specified as 5/16" ± 0.005", meaning the actual dimension can vary between 0.3075" and 0.3175". Understanding tolerances is essential for ensuring parts fit correctly and function as intended.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
-
Misreading fractions: Carefully examine the fractions to avoid misinterpreting the values. Double-checking your measurements is always a good practice.
-
Using incorrect tools: Ensure you use the appropriate measuring tools, such as a ruler or caliper, to accurately determine the measurements.
-
Ignoring tolerances: When working with precision parts, always consider the acceptable tolerances to ensure compatibility and functionality.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Can I use 5/16" where 3/16" is specified?
A: Generally, no. Using a larger dimension where a smaller one is specified will likely result in a loose fit, impacting functionality and potentially causing damage.
Q: Can I use 3/16" where 5/16" is specified?
A: No. Using a smaller dimension where a larger one is specified will result in a tight or impossible fit. This could damage the parts and prevent proper assembly.
Q: How can I accurately measure 3/16" and 5/16"?
A: Use a ruler with 1/16" markings or a digital caliper for accurate measurements.
Q: What is the difference in area between a 3/16" and 5/16" circle?
A: The area difference would be significant, as area is calculated using the square of the radius (πr²). The larger radius of the 5/16" circle would lead to a considerably larger area compared to the 3/16" circle. This difference is critical in applications involving surface area calculations.
Q: Are there metric equivalents for 3/16" and 5/16"?
A: Yes, approximate metric equivalents are: 3/16" ≈ 4.76 mm and 5/16" ≈ 7.94 mm. However, it’s always best to use the precise fractional inch measurement when working with imperial units.
Conclusion: Precision Matters
The difference between 3/16" and 5/16", while seemingly minor, is critical in numerous applications. Understanding the numerical values, decimal equivalents, and practical implications of each measurement is essential for success in any field involving precision work. Always double-check your measurements, use the correct tools, and consider tolerances to avoid errors and ensure the desired outcome. Mastering fractional inches is a fundamental skill for anyone working with measurements and dimensions. By understanding the nuances and implications of these seemingly small differences, you'll enhance your proficiency and build more accurate and reliable projects. Remember, precision is paramount when it comes to measurements, and the difference between these two seemingly small measurements can mean the difference between success and failure.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Hcf Of 8 And 12
Sep 24, 2025
-
20 25 As A Percent
Sep 24, 2025
-
Whats 30 Off Of 60
Sep 24, 2025
-
What Is 119 Divisible By
Sep 24, 2025
-
45 Degrees Celsius To F
Sep 24, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 3 16 Vs 5 16 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.