30/4 As A Mixed Number
horsecheck
Sep 17, 2025 · 5 min read
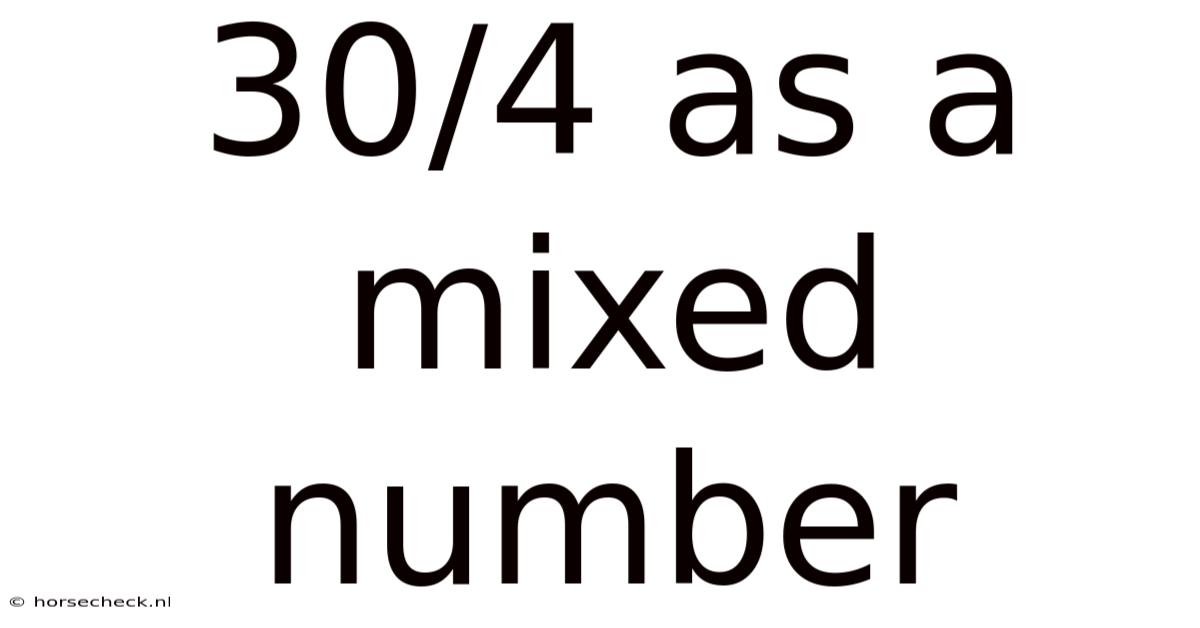
Table of Contents
Understanding 30/4 as a Mixed Number: A Comprehensive Guide
The seemingly simple fraction 30/4 can be a stumbling block for many, especially those new to working with fractions. This comprehensive guide will not only show you how to convert 30/4 into a mixed number but also delve into the underlying concepts, providing a solid foundation for understanding fractions and mixed numbers. We'll explore the process step-by-step, explain the mathematical reasoning behind it, and answer frequently asked questions to ensure a complete understanding. This guide aims to be a valuable resource for students, educators, and anyone looking to solidify their grasp of fraction manipulation.
What are Mixed Numbers?
Before we tackle 30/4 specifically, let's define what a mixed number is. A mixed number combines a whole number and a proper fraction. A proper fraction is a fraction where the numerator (the top number) is smaller than the denominator (the bottom number). For example, 1/2, 3/4, and 7/8 are all proper fractions. A mixed number represents a quantity that is greater than one. For example, 2 ½ represents two whole units and one-half of another unit.
Converting Improper Fractions to Mixed Numbers
The fraction 30/4 is an improper fraction. An improper fraction is one where the numerator is greater than or equal to the denominator. To understand 30/4, we need to convert it into a mixed number. This involves dividing the numerator by the denominator.
Step-by-step conversion of 30/4:
-
Divide the numerator by the denominator: Divide 30 by 4. This gives us a quotient of 7 and a remainder of 2.
-
Write the quotient as the whole number: The quotient (7) becomes the whole number part of the mixed number.
-
Write the remainder as the numerator: The remainder (2) becomes the numerator of the fraction part.
-
Keep the original denominator: The denominator (4) remains unchanged.
Therefore, 30/4 as a mixed number is 7 2/4.
Simplifying the Mixed Number
While 7 2/4 is a correct representation, it's not in its simplest form. We can simplify the fraction part (2/4) by finding the greatest common divisor (GCD) of the numerator and denominator. The GCD of 2 and 4 is 2. Dividing both the numerator and the denominator by 2, we get:
2 ÷ 2 = 1 4 ÷ 2 = 2
So, 2/4 simplifies to 1/2.
Therefore, the simplest form of 30/4 as a mixed number is 7 ½.
Visualizing the Conversion
Imagine you have 30 cookies, and you want to divide them equally among 4 friends. You can give each friend 7 cookies (7 x 4 = 28 cookies). You'll have 2 cookies left over (30 - 28 = 2). Each friend gets 7 whole cookies, and you have 2 cookies remaining to be divided among the 4 friends, representing the fraction 2/4, which simplifies to ½. This visually demonstrates how 30/4 equals 7 ½.
The Mathematical Explanation
The conversion from an improper fraction to a mixed number is fundamentally based on the division algorithm. The division algorithm states that for any two integers a (numerator) and b (denominator), where b is not zero, there exist unique integers q (quotient) and r (remainder) such that:
a = b * q + r, where 0 ≤ r < b
In our case, a = 30 and b = 4. When we divide 30 by 4, we get:
30 = 4 * 7 + 2
The quotient (7) represents the whole number part of the mixed number, and the remainder (2) represents the numerator of the fractional part. The denominator remains 4. This mathematically justifies the conversion process.
Working with Mixed Numbers: Addition and Subtraction
Once you have converted 30/4 to the mixed number 7 ½, you can perform various arithmetic operations. Let's look at addition and subtraction with mixed numbers.
Addition: To add mixed numbers, you add the whole number parts separately and the fractional parts separately. For example, let's add 7 ½ and 2 ¼:
7 ½ + 2 ¼ = (7 + 2) + (½ + ¼) = 9 + (2/4 + 1/4) = 9 + 3/4 = 9 ¾
Subtraction: Subtraction follows a similar pattern. Let's subtract 2 ¼ from 7 ½:
7 ½ - 2 ¼ = (7 - 2) + (½ - ¼) = 5 + (2/4 - 1/4) = 5 + 1/4 = 5 ¼
Working with Mixed Numbers: Multiplication and Division
Multiplication and division of mixed numbers require a slightly different approach. It is generally easier to convert the mixed numbers into improper fractions before performing these operations.
Multiplication: Let's multiply 7 ½ by 2:
First, convert 7 ½ to an improper fraction: (7 x 2) + 1 = 15/2
Then, multiply: (15/2) x 2 = 15
Division: Let's divide 7 ½ by 2:
Again, convert 7 ½ to an improper fraction: 15/2
Then, divide: (15/2) ÷ 2 = (15/2) x (1/2) = 15/4 = 3 ¾
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Why is it important to simplify fractions?
A1: Simplifying fractions makes them easier to understand and work with. It presents the fraction in its most concise and efficient form.
Q2: Can I convert any improper fraction into a mixed number?
A2: Yes, as long as the denominator is not zero.
Q3: What if the remainder is zero after dividing the numerator by the denominator?
A3: If the remainder is zero, the improper fraction is actually a whole number. For example, 12/4 = 3.
Q4: Are there other ways to represent 30/4?
A4: Yes, you could also represent it as a decimal (7.5).
Q5: How do I choose between using a mixed number and an improper fraction?
A5: The choice depends on the context of the problem. Improper fractions are often more convenient for multiplication and division, while mixed numbers are often preferred for representing quantities in real-world situations.
Conclusion
Converting 30/4 to a mixed number (7 ½) is a fundamental skill in mathematics. Understanding this process not only helps in solving numerical problems but also provides a solid foundation for working with fractions and mixed numbers in various mathematical operations. By mastering this concept, you build a stronger understanding of numbers and their representation, paving the way for tackling more complex mathematical challenges. Remember, practice is key! The more you work with fractions and mixed numbers, the more comfortable and confident you will become. This guide aims to provide a clear and thorough understanding, leaving you equipped to confidently handle similar fraction conversions in the future.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 30/4 As A Mixed Number . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.