47/6 As A Mixed Number
horsecheck
Sep 18, 2025 · 5 min read
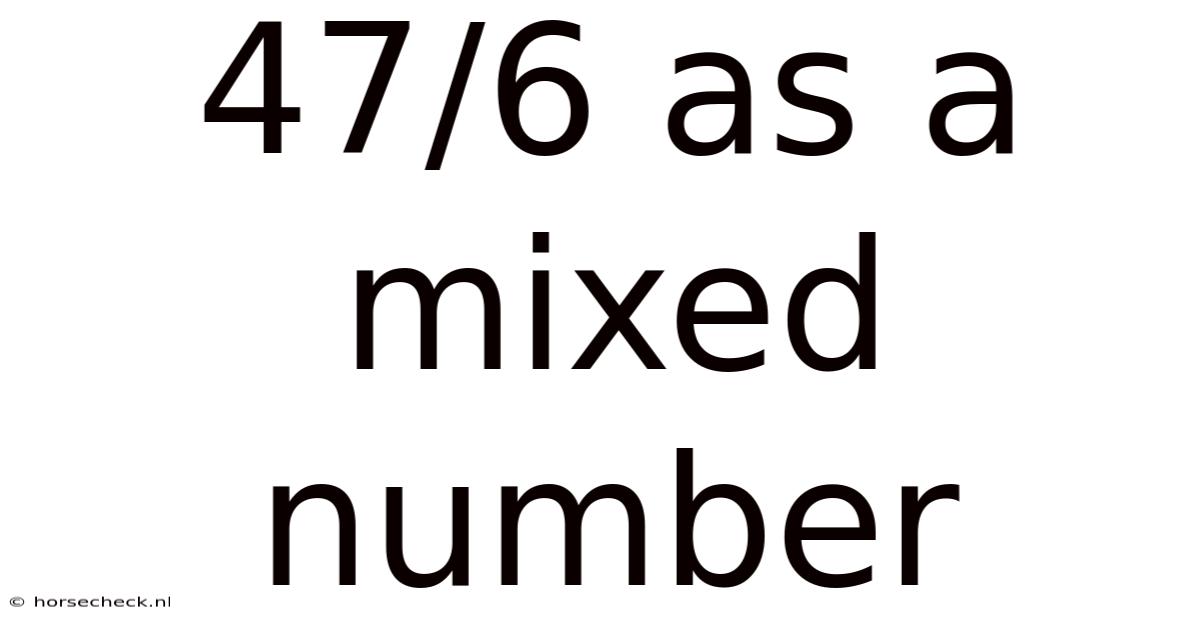
Table of Contents
Understanding 47/6 as a Mixed Number: A Comprehensive Guide
Many mathematical operations involve the conversion of improper fractions, like 47/6, into mixed numbers. This conversion is crucial for simplifying calculations, visualizing quantities, and gaining a deeper understanding of fractional representations. This comprehensive guide will delve into the process of converting 47/6 into a mixed number, exploring the underlying mathematical principles and providing practical examples to solidify your understanding. We'll also address common misconceptions and frequently asked questions.
Understanding Fractions and Mixed Numbers
Before we dive into converting 47/6, let's refresh our understanding of fractions and mixed numbers.
A fraction represents a part of a whole. It's composed of two numbers: the numerator (the top number) and the denominator (the bottom number). The denominator indicates how many equal parts the whole is divided into, while the numerator indicates how many of those parts are being considered.
An improper fraction is a fraction where the numerator is greater than or equal to the denominator (e.g., 47/6). This indicates that the fraction represents a quantity greater than or equal to one whole.
A mixed number combines a whole number and a proper fraction (a fraction where the numerator is less than the denominator, e.g., 1/2). It provides a more intuitive representation of quantities greater than one. For instance, 7 1/2 represents seven whole units and one-half of another unit.
Converting 47/6 to a Mixed Number: Step-by-Step Guide
Converting an improper fraction like 47/6 to a mixed number involves dividing the numerator by the denominator. Here's a step-by-step guide:
Step 1: Perform the Division
Divide the numerator (47) by the denominator (6):
47 ÷ 6 = 7 with a remainder of 5
Step 2: Identify the Whole Number and the Remainder
The quotient (the result of the division) becomes the whole number part of the mixed number. In this case, the quotient is 7.
The remainder (the amount left over after the division) becomes the numerator of the fractional part of the mixed number. Here, the remainder is 5.
Step 3: Construct the Mixed Number
The denominator of the fractional part remains the same as the denominator of the original improper fraction (6).
Therefore, the mixed number representation of 47/6 is 7 5/6.
Visualizing the Conversion
Imagine you have 47 identical objects. If you want to group these objects into sets of 6, you can create 7 complete sets (7 x 6 = 42 objects). You'll have 5 objects remaining (47 - 42 = 5). This visually represents 7 whole sets and 5/6 of another set, mirroring the mixed number 7 5/6.
The Mathematical Principle Behind the Conversion
The conversion from an improper fraction to a mixed number is based on the principle of equivalent fractions and the distributive property of multiplication over addition.
Consider the improper fraction 47/6. We can express this as:
47/6 = (42 + 5)/6
Using the distributive property, we can separate this into:
42/6 + 5/6
Since 42/6 simplifies to 7, we get:
7 + 5/6 = 7 5/6
Converting Back to an Improper Fraction
It's essential to understand how to convert a mixed number back into an improper fraction. This is useful for performing calculations involving mixed numbers. The process is as follows:
- Multiply the whole number by the denominator: 7 * 6 = 42
- Add the numerator: 42 + 5 = 47
- Keep the denominator the same: The denominator remains 6.
Therefore, 7 5/6 converts back to the improper fraction 47/6.
Practical Applications of Mixed Numbers
Mixed numbers are frequently used in various real-world scenarios:
- Measurement: Measuring lengths, weights, or volumes often results in mixed numbers (e.g., 2 1/2 inches).
- Cooking and Baking: Recipes commonly utilize mixed numbers to specify ingredient quantities (e.g., 1 1/4 cups of flour).
- Construction: Building projects often involve measurements and calculations using mixed numbers.
- Data Analysis: Representing data using mixed numbers can provide a more intuitive understanding of the values.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
A common mistake when converting improper fractions to mixed numbers is forgetting to include the remainder as the numerator of the fractional part. Always carefully perform the division and correctly identify the quotient and remainder. Another mistake is incorrectly converting back to an improper fraction – remember to multiply the whole number by the denominator before adding the numerator.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Can all improper fractions be converted into mixed numbers?
A1: Yes, all improper fractions can be converted into mixed numbers.
Q2: What if the remainder is 0 after the division?
A2: If the remainder is 0, it means the improper fraction is a whole number. For example, 12/3 = 4, with no remainder, so the mixed number representation is simply 4.
Q3: Is there a faster way to convert large improper fractions?
A3: While the division method is straightforward, for very large numbers, a calculator can expedite the process, although understanding the underlying principles remains crucial.
Q4: Why is it important to learn this conversion?
A4: Converting between improper fractions and mixed numbers is fundamental in various mathematical contexts and real-world applications, simplifying calculations and enhancing comprehension.
Conclusion
Converting 47/6 to the mixed number 7 5/6 is a fundamental skill in mathematics. Understanding this process, the underlying principles, and the ability to convert back and forth between improper fractions and mixed numbers is essential for proficiency in arithmetic and broader mathematical applications. Mastering this conversion enhances problem-solving capabilities and improves your overall understanding of fractional representation. By practicing the steps outlined in this guide and addressing the common pitfalls, you can confidently navigate the world of fractions and mixed numbers. Remember, the key is to grasp the underlying concepts, not just memorize the steps. This understanding will pave the way for more advanced mathematical concepts.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 47/6 As A Mixed Number . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.