64/5 As A Mixed Number
horsecheck
Sep 16, 2025 · 6 min read
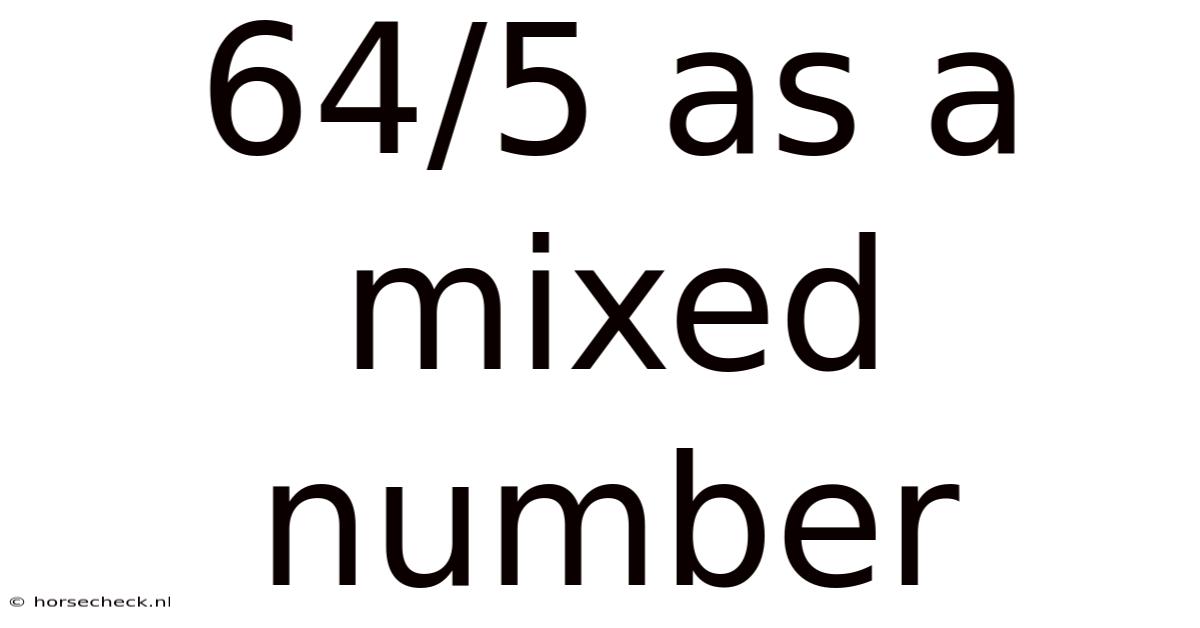
Table of Contents
Understanding 64/5 as a Mixed Number: A Comprehensive Guide
Converting improper fractions, like 64/5, into mixed numbers is a fundamental skill in mathematics. This comprehensive guide will not only show you how to convert 64/5 into a mixed number but will also delve into the underlying concepts, provide practical examples, and address frequently asked questions. Mastering this skill is crucial for a strong foundation in arithmetic and algebra. Understanding fractions and mixed numbers is essential for various applications, from baking recipes to advanced engineering calculations.
What is a Mixed Number?
Before we dive into converting 64/5, let's clarify what a mixed number is. A mixed number combines a whole number and a proper fraction. A proper fraction is a fraction where the numerator (the top number) is smaller than the denominator (the bottom number). For example, 2 ¾ is a mixed number; it represents two whole units and three-quarters of another unit. Understanding mixed numbers is vital because they offer a more intuitive representation of quantities than improper fractions, especially in real-world contexts.
Converting Improper Fractions to Mixed Numbers
An improper fraction is a fraction where the numerator is greater than or equal to the denominator. The fraction 64/5 is an improper fraction because 64 (the numerator) is larger than 5 (the denominator). To convert an improper fraction to a mixed number, we need to determine how many whole units are contained within the fraction and the remaining fractional part. This process involves division.
Steps to Convert 64/5 to a Mixed Number
Here's a step-by-step guide on how to convert the improper fraction 64/5 into a mixed number:
-
Divide the Numerator by the Denominator: We start by dividing the numerator (64) by the denominator (5).
64 ÷ 5 = 12 with a remainder of 4
-
Identify the Whole Number: The quotient (the result of the division) becomes the whole number part of our mixed number. In this case, the quotient is 12.
-
Identify the Numerator of the Fraction: The remainder from the division becomes the numerator of the fractional part of our mixed number. Here, the remainder is 4.
-
Keep the Original Denominator: The denominator of the fraction in the mixed number remains the same as the denominator of the original improper fraction. So, our denominator is 5.
-
Combine the Whole Number and the Fraction: Combine the whole number and the fraction to form the mixed number. Therefore, 64/5 as a mixed number is 12 ⁴⁄₅.
Visualizing the Conversion
Imagine you have 64 identical items, and you want to group them into sets of 5. You can create 12 complete sets of 5, leaving you with 4 items remaining. This remaining 4 items represent the ⁴⁄₅ part of a complete set. This visual representation reinforces the concept of converting an improper fraction into a mixed number.
Practical Applications of Mixed Numbers
Mixed numbers are widely used in various real-world scenarios. Here are a few examples:
-
Cooking and Baking: Recipes often call for mixed numbers, such as 2 ½ cups of flour or 1 ¾ teaspoons of baking powder. Understanding mixed numbers is crucial for accurate measurements and successful baking.
-
Measurements: Measuring lengths, weights, and volumes frequently involves mixed numbers. For instance, a board might measure 3 ⁵⁄₈ feet long or a container might hold 1 ¼ gallons of liquid.
-
Construction and Engineering: Precision in construction and engineering relies heavily on accurate measurements, which often involve mixed numbers. This is particularly relevant in projects that require intricate detail and precise fitting of parts.
-
Everyday Calculations: Many daily calculations, from calculating the cost of items to determining distances, might involve fractions and mixed numbers. Being comfortable with these concepts enhances mathematical skills in everyday life.
Further Exploration: Working with Mixed Numbers
Once you've mastered converting improper fractions to mixed numbers, you'll need to learn how to perform various operations with mixed numbers, including:
-
Adding Mixed Numbers: This involves adding the whole numbers and then separately adding the fractions, simplifying the result if necessary.
-
Subtracting Mixed Numbers: Similar to addition, subtraction involves subtracting the whole numbers and the fractions separately, potentially borrowing from the whole number if needed.
-
Multiplying Mixed Numbers: Convert the mixed numbers into improper fractions before multiplying, and then simplify the result.
-
Dividing Mixed Numbers: Again, convert the mixed numbers into improper fractions before dividing, and simplify the result.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Why is it important to convert improper fractions to mixed numbers?
A: While improper fractions are perfectly valid mathematical representations, mixed numbers often provide a more intuitive and easily understandable way to represent quantities in real-world contexts. They're easier to visualize and work with in many practical situations.
Q: Can I leave an answer as an improper fraction?
A: Yes, mathematically, an improper fraction is just as correct as a mixed number. However, in many practical applications, mixed numbers offer a clearer and more usable representation of the quantity. The context dictates the most appropriate form.
Q: What if the remainder is zero after dividing the numerator by the denominator?
A: If the remainder is zero, it means the original fraction was already a whole number. For instance, if you had 10/5, the division would result in 2 with a remainder of 0. Therefore, the mixed number would simply be 2.
Q: How can I check my work when converting an improper fraction to a mixed number?
A: You can check your work by converting the mixed number back into an improper fraction. To do this, multiply the whole number by the denominator, add the numerator, and place the result over the original denominator. If you obtain the original improper fraction, your conversion is correct. For example, for 12 ⁴⁄₅: (12 * 5) + 4 = 64, so the improper fraction is 64/5.
Q: Are there any online tools or calculators that can help me convert improper fractions to mixed numbers?
A: While many online calculators exist that perform this conversion, the understanding of the underlying process is crucial. Relying solely on calculators without grasping the method limits your mathematical understanding. Developing your own skill in performing the conversion is far more beneficial.
Conclusion
Converting an improper fraction like 64/5 to a mixed number (12 ⁴⁄₅) is a straightforward process involving division, identification of the whole number and fractional parts, and combining them into a mixed number format. This skill is fundamental to various mathematical applications and is crucial for navigating real-world scenarios involving fractions. Understanding the process and practicing conversion will greatly improve your numerical literacy and build a stronger foundation in mathematics. Remember, while calculators can be helpful, mastering the manual method is key to developing a deep understanding of the concepts. Keep practicing, and you'll soon find converting improper fractions to mixed numbers becomes second nature!
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 64/5 As A Mixed Number . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.