Gcf Of 25 And 45
horsecheck
Sep 18, 2025 · 6 min read
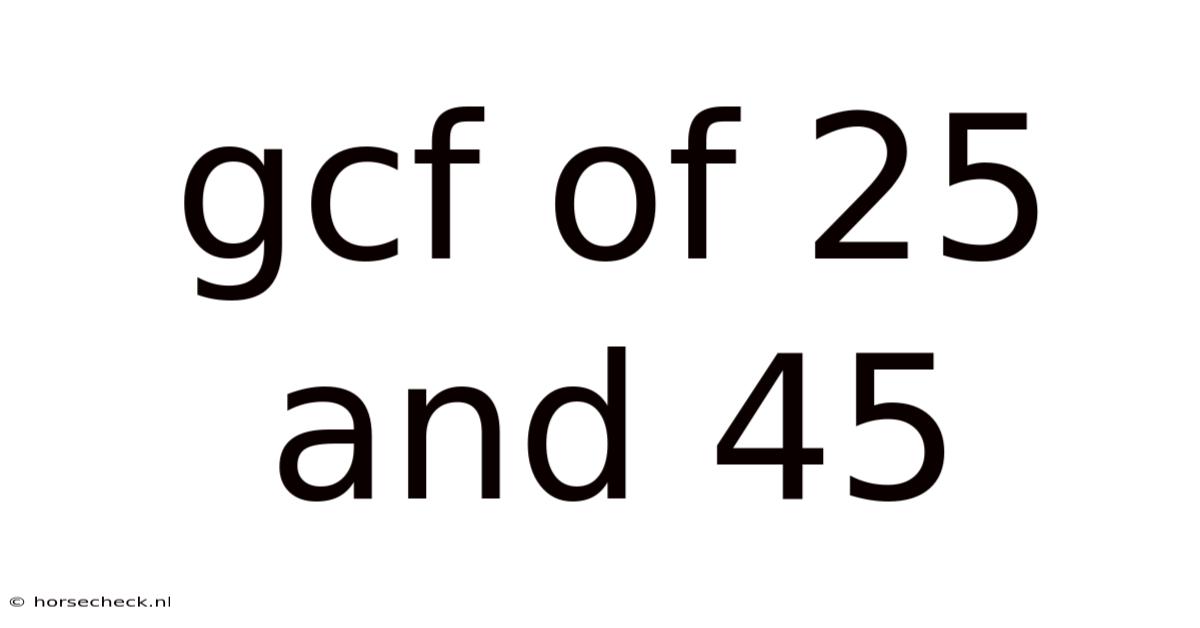
Table of Contents
Finding the Greatest Common Factor (GCF) of 25 and 45: A Comprehensive Guide
Finding the greatest common factor (GCF), also known as the greatest common divisor (GCD), of two numbers is a fundamental concept in mathematics. This article will explore various methods to determine the GCF of 25 and 45, providing a detailed explanation suitable for students of all levels, from elementary school to high school. We'll delve into the underlying principles, examine different techniques, and answer frequently asked questions to ensure a complete understanding of this crucial mathematical skill. Understanding GCF is essential for simplifying fractions, solving algebraic equations, and tackling more advanced mathematical concepts.
Understanding Greatest Common Factor (GCF)
Before we dive into calculating the GCF of 25 and 45, let's define the term. The greatest common factor (GCF) of two or more numbers is the largest number that divides evenly into all of them without leaving a remainder. For instance, the GCF of 12 and 18 is 6 because 6 is the largest number that divides both 12 and 18 perfectly. Finding the GCF is a crucial skill in simplifying fractions and solving various mathematical problems.
Method 1: Listing Factors
The simplest method to find the GCF is by listing all the factors of each number and identifying the largest common factor.
Step 1: List the factors of 25.
Factors are numbers that divide evenly into a given number. The factors of 25 are 1, 5, and 25.
Step 2: List the factors of 45.
The factors of 45 are 1, 3, 5, 9, 15, and 45.
Step 3: Identify common factors.
Comparing the lists, we see that the common factors of 25 and 45 are 1 and 5.
Step 4: Determine the greatest common factor.
The largest of these common factors is 5. Therefore, the GCF of 25 and 45 is 5.
Method 2: Prime Factorization
Prime factorization involves expressing a number as a product of its prime factors. Prime numbers are whole numbers greater than 1 that are only divisible by 1 and themselves (e.g., 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, etc.). This method is particularly useful for larger numbers.
Step 1: Find the prime factorization of 25.
25 can be written as 5 x 5, or 5².
Step 2: Find the prime factorization of 45.
45 can be written as 3 x 3 x 5, or 3² x 5.
Step 3: Identify common prime factors.
Comparing the prime factorizations, we see that both 25 and 45 share one common prime factor: 5.
Step 4: Calculate the GCF.
To find the GCF, we multiply the common prime factors together. In this case, the only common prime factor is 5. Therefore, the GCF of 25 and 45 is 5.
Method 3: Euclidean Algorithm
The Euclidean algorithm is an efficient method for finding the GCF of two numbers, especially when dealing with larger numbers. It's based on the principle that the GCF of two numbers does not change if the larger number is replaced by its difference with the smaller number. This process is repeated until the two numbers are equal.
Step 1: Divide the larger number (45) by the smaller number (25).
45 ÷ 25 = 1 with a remainder of 20.
Step 2: Replace the larger number with the remainder.
Now we find the GCF of 25 and 20.
Step 3: Repeat the process.
25 ÷ 20 = 1 with a remainder of 5.
Step 4: Repeat again.
20 ÷ 5 = 4 with a remainder of 0.
Step 5: The GCF is the last non-zero remainder.
Since the remainder is 0, the GCF is the previous remainder, which is 5. Therefore, the GCF of 25 and 45 is 5.
Illustrative Example: Real-world Application of GCF
Imagine you're making gift bags for a party. You have 25 red candies and 45 blue candies. You want to divide the candies evenly into gift bags, with each bag containing the same number of red and blue candies. To determine the maximum number of gift bags you can make, you need to find the GCF of 25 and 45. As we've established, the GCF is 5. This means you can make 5 gift bags, each containing 5 red candies and 9 blue candies (25/5 = 5 and 45/5 = 9).
Mathematical Properties and Significance of GCF
The concept of GCF plays a vital role in various areas of mathematics:
-
Simplifying Fractions: The GCF is crucial in simplifying fractions to their lowest terms. For example, the fraction 25/45 can be simplified by dividing both the numerator and denominator by their GCF (5), resulting in the equivalent fraction 5/9.
-
Solving Equations: GCF is often used in solving algebraic equations and simplifying expressions. Factoring polynomials often relies on finding the GCF of the terms involved.
-
Number Theory: GCF is a fundamental concept in number theory, used in exploring relationships between numbers and their divisors.
-
Modular Arithmetic: The concept of GCF underpins modular arithmetic, a system of arithmetic for integers where numbers "wrap around" upon reaching a certain value (the modulus). It is particularly important in cryptography.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What if the GCF of two numbers is 1?
If the GCF of two numbers is 1, the numbers are considered relatively prime or coprime. This means they share no common factors other than 1.
Q2: Can the GCF of two numbers be larger than either number?
No. The GCF of two numbers can never be larger than the smaller of the two numbers.
Q3: Are there other methods for finding the GCF?
Yes, there are other more advanced algorithms like the binary GCD algorithm and the extended Euclidean algorithm, but they are usually employed for very large numbers or in computer programming.
Q4: Why is finding the GCF important?
Finding the GCF is a fundamental skill with wide applications in various mathematical contexts, from simplifying fractions to solving complex equations and understanding number theory.
Conclusion
Finding the greatest common factor (GCF) of 25 and 45, which is 5, can be achieved through multiple methods, each offering a unique approach to problem-solving. The methods explored – listing factors, prime factorization, and the Euclidean algorithm – demonstrate the versatility and importance of understanding GCF. Mastering these techniques not only helps solve immediate problems but also lays a strong foundation for more advanced mathematical concepts. Understanding the GCF is a cornerstone of mathematical proficiency, applicable across various fields and levels of mathematical study. Its applications extend far beyond simple arithmetic, highlighting its significance in diverse mathematical disciplines. The ability to efficiently calculate the GCF is an invaluable tool for any student or mathematician.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Gcf Of 25 And 45 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.