What Is 12 / 6
horsecheck
Sep 17, 2025 · 6 min read
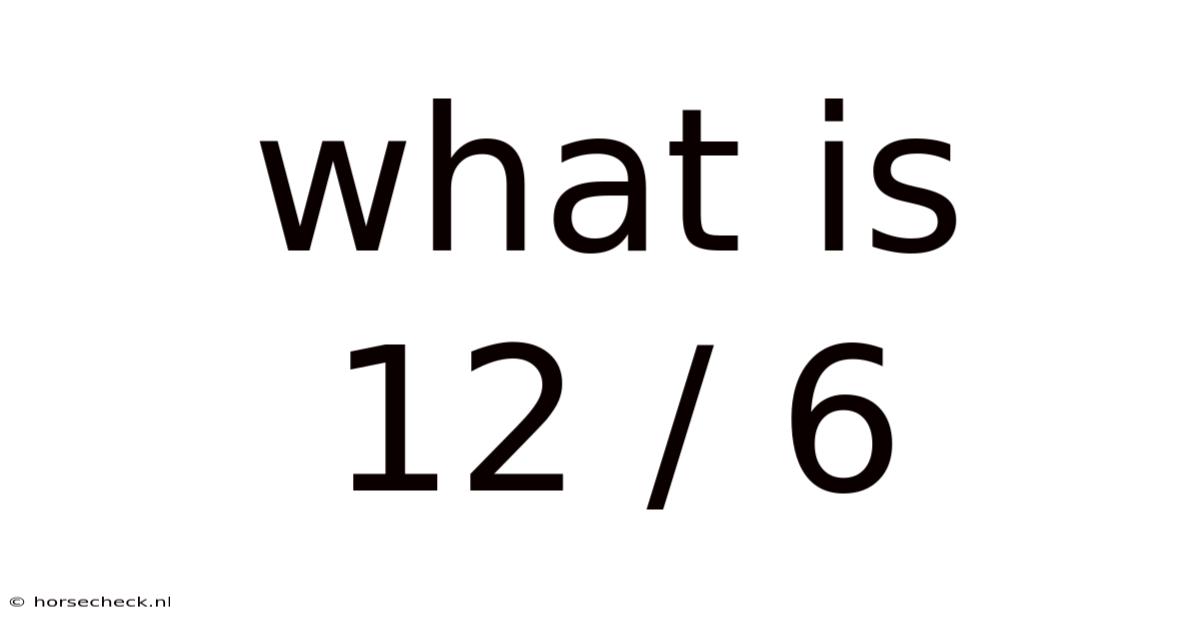
Table of Contents
What is 12 / 6? A Deep Dive into Division and its Applications
What is 12 / 6? This seemingly simple question opens the door to a fascinating exploration of division, one of the fundamental operations in mathematics. While the answer itself is straightforward – 2 – understanding why the answer is 2 unlocks a deeper understanding of mathematical concepts that extend far beyond basic arithmetic. This article will not only answer the question but delve into the principles behind division, explore its various applications, and address common misconceptions. We will also examine the concept of division in different contexts, from everyday situations to advanced mathematical fields.
Understanding Division: More Than Just Sharing
At its core, division is the process of splitting a quantity into equal parts. When we say 12 / 6, we are asking: "If we have 12 objects and we want to divide them into 6 equal groups, how many objects will be in each group?" The answer, 2, represents the size of each group.
Think of it practically. Imagine you have 12 cookies and you want to share them equally among 6 friends. To find out how many cookies each friend gets, you perform the division: 12 / 6 = 2. Each friend receives 2 cookies. This simple example highlights the practical application of division in everyday life.
The Relationship Between Division and Multiplication
Division and multiplication are inverse operations. This means they undo each other. If we know that 6 x 2 = 12, then we also know that 12 / 6 = 2 and 12 / 2 = 6. This relationship is crucial for understanding and solving division problems. It allows us to use multiplication as a tool to check our division answers and vice versa. For example, after calculating 12 / 6 = 2, we can verify this by multiplying 6 x 2 to confirm the result is 12.
Different Ways to Represent Division
The division symbol "/" is just one way to represent division. Other notations include:
- The division sign (÷): 12 ÷ 6 = 2
- A fraction: 12/6 = 2 This representation emphasizes the concept of a ratio or part of a whole.
Understanding these different representations is essential, as they are frequently used in various mathematical contexts and problems.
Exploring Division with Different Numbers
Let's expand our understanding by considering other division problems. The principle remains the same – dividing a quantity into equal parts.
- 15 / 3 = 5: If you have 15 apples and divide them into 3 equal groups, each group contains 5 apples.
- 20 / 4 = 5: Similarly, if you have 20 oranges and divide them into 4 equal groups, each group contains 5 oranges.
- 24 / 8 = 3: Dividing 24 pencils into 8 equal groups results in 3 pencils per group.
These examples demonstrate the versatility of division and how it applies to a variety of situations involving different quantities and numbers of groups.
Division with Remainders
Not all division problems result in a whole number answer. Sometimes, there's a remainder – a number left over after the division is complete.
Consider 13 / 4. We can fit three 4s into 13 (3 x 4 = 12), but there's 1 left over. We can represent this as:
- 13 / 4 = 3 with a remainder of 1
- or, 13 / 4 = 3 R 1
Understanding remainders is essential for solving more complex division problems and for understanding concepts in number theory and modular arithmetic.
Division in Different Number Systems
While we've focused on division with whole numbers, the concept extends to other number systems:
- Decimals: 12.5 / 2.5 = 5 Division with decimals requires a slightly different approach but follows the same fundamental principle.
- Fractions: (1/2) / (1/4) = 2 Dividing fractions involves multiplying by the reciprocal of the second fraction.
- Negative Numbers: -12 / 6 = -2 and 12 / -6 = -2. The rules for signs in division are similar to those in multiplication: a positive number divided by a negative number (or vice versa) results in a negative number. A negative number divided by a negative number results in a positive number.
Mastering division in these various number systems provides a more complete and robust mathematical foundation.
Applications of Division in Real Life
Division isn't just a mathematical concept; it's a tool used extensively in various real-world scenarios:
- Sharing equally: Dividing resources fairly among individuals or groups.
- Calculating averages: Finding the average score on a test or the average speed of a journey.
- Scaling recipes: Adjusting recipe quantities for different numbers of servings.
- Unit conversions: Converting units of measurement (e.g., kilometers to meters).
- Calculating ratios and proportions: Understanding the relationship between different quantities.
- Finance: Calculating interest rates, splitting bills, determining profit margins.
- Engineering and physics: Solving numerous problems involving proportions, rates, and ratios.
These examples showcase the practical relevance and widespread application of division in our daily lives and various professional fields.
Division in Advanced Mathematics
Division plays a crucial role in more advanced mathematical concepts:
- Algebra: Solving algebraic equations often involves division to isolate variables.
- Calculus: Differentiation and integration involve limits and derivatives, which often utilize division.
- Number Theory: Division is fundamental to understanding prime numbers, divisibility rules, and modular arithmetic.
- Abstract Algebra: Division (or its equivalent) is a key component of group theory and ring theory.
The seemingly simple operation of division forms the basis for many complex mathematical concepts and theories.
Common Misconceptions about Division
Several misconceptions can hinder a proper understanding of division:
- Division by zero: Dividing by zero is undefined. There is no numerical answer because it's impossible to divide a quantity into zero groups. Attempting to do so leads to mathematical inconsistencies and errors.
- Order of operations: Division should be performed before addition or subtraction, unless parentheses or brackets dictate otherwise. Understanding the order of operations (PEMDAS/BODMAS) is crucial for accurate calculations.
- Interpreting remainders: Understanding how to interpret and use remainders in real-world contexts is vital. For example, a remainder in a problem involving sharing cookies might indicate that some cookies are left over.
Addressing these common misconceptions ensures a clearer understanding of division and its application.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Q: What happens when you divide a smaller number by a larger number?
A: The result will be a decimal or fraction less than 1. For example, 3 / 5 = 0.6 or 3/5.
- Q: Is division commutative?
A: No, division is not commutative. This means that the order of the numbers matters. 12 / 6 is not the same as 6 / 12.
- Q: Is division associative?
A: No, division is not associative. This means that the grouping of numbers affects the result. (12 / 6) / 2 is not the same as 12 / (6 / 2).
- Q: How can I improve my division skills?
A: Practice is key. Start with simple problems and gradually increase the complexity. Use different methods and representations of division to strengthen your understanding.
- Q: What are some real-world examples of division beyond the ones mentioned?
A: Calculating fuel efficiency (miles per gallon), determining the price per unit of an item, calculating the average speed, and determining the number of doses from a given amount of medication.
Conclusion: Beyond the Simple Answer
The question "What is 12 / 6?" initially seems trivial. However, exploring this question thoroughly unveils a wealth of mathematical concepts, from the fundamental principles of division to its sophisticated applications in advanced mathematics and real-world problem-solving. By understanding the underlying principles and addressing common misconceptions, we can unlock a deeper appreciation for this crucial arithmetic operation and its widespread significance. Remember, mathematics is not just about finding answers but also about understanding the processes and reasoning behind them. So, while 12 / 6 = 2 is a simple answer, the journey to understand it reveals a profound understanding of the mathematical world around us.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is 12 / 6 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.