25 64 Vs 3 8
horsecheck
Sep 22, 2025 · 6 min read
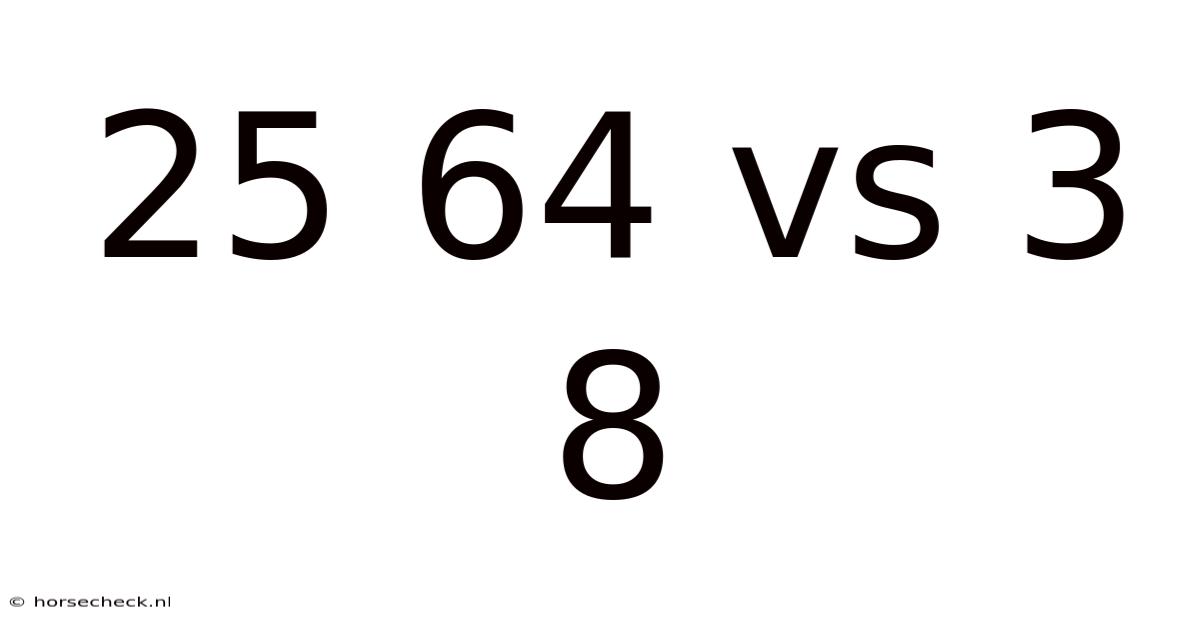
Table of Contents
2564 vs 38: A Deep Dive into Bit Depth and its Impact on Audio and Image Quality
Understanding the difference between 2564 and 38 might seem daunting at first glance, especially if you're not immersed in the world of digital audio or image processing. These numbers represent bit depth, a crucial parameter determining the quality and fidelity of digital media. This article will delve into the intricacies of bit depth, explaining what it means, how it affects audio and images, and why the difference between 2564 (often a misunderstanding, likely meant to be 24-bit) and 38 (likely referring to a highly compressed format) is so significant. We'll explore the technical aspects while keeping the explanations accessible to everyone, regardless of their technical background.
What is Bit Depth?
In the digital world, information—be it audio or image data—is represented using binary code: a sequence of 0s and 1s. Bit depth signifies the number of bits used to represent each sample of audio or each pixel of an image. Each bit doubles the number of possible values. For instance:
- 1-bit: Offers only two possible values (0 or 1), resulting in very low resolution and extremely limited detail. Think of a very basic black and white image.
- 8-bit: Allows for 2<sup>8</sup> = 256 different values. This is commonly found in older image formats and some lower-quality audio.
- 16-bit: Offers 2<sup>16</sup> = 65,536 values. This is a standard for CD-quality audio and many image formats.
- 24-bit: Provides 2<sup>24</sup> = 16,777,216 values. This is considered high-resolution audio and image quality, offering a much wider dynamic range and subtle detail.
- 32-bit: Offers 2<sup>32</sup> = 4,294,967,296 values. Often used in professional audio applications for its extensive dynamic range and reduced quantization noise.
Therefore, 2564 (likely a typo for 24-bit) represents a much higher bit depth than 38 (potentially indicating a highly compressed format with a low bit depth, perhaps in the range of 4-bit or less). The higher the bit depth, the more accurately the original analog signal is represented in the digital domain. This leads to significantly improved quality.
Bit Depth in Audio: The Sound of Silence and the Roar of Detail
In audio, each sample represents the amplitude of the sound wave at a specific point in time. A higher bit depth means a larger number of amplitude levels can be captured, leading to a more nuanced and detailed representation of the sound.
24-bit audio (or the intended meaning of 2564): Captures subtle nuances in the sound, resulting in a richer, more realistic audio experience. This higher resolution reduces quantization noise (a type of distortion that occurs when converting analog to digital) considerably, leading to a cleaner and more transparent sound. You'll hear a wider dynamic range, from the quietest whispers to the loudest explosions, all reproduced with impressive fidelity. The detail in the instruments and vocals becomes strikingly clear.
Low bit-depth audio (like the implied 38): With a very low bit depth, a significant amount of audio information is lost during the conversion process. This results in a noticeably compressed, distorted, and less dynamic sound. The lack of detail makes the audio sound "thin" and lacks the richness and fullness of higher bit-depth audio. Quantization noise becomes significantly more audible, creating an unpleasant background hiss or distortion. Think of the sound quality of an old AM radio compared to a modern high-fidelity system.
Bit Depth in Images: From Pixelated to Photorealistic
In image processing, each pixel's color is represented by a value determined by the bit depth. Higher bit depths allow for a smoother gradation of colors and finer details.
24-bit images (or the intended meaning of 2564): Employ 24 bits to represent each pixel's color information (typically using 8 bits per color channel: Red, Green, and Blue). This results in vibrant, detailed, and realistic images. Smooth transitions between colors are evident, and fine details are sharply defined. There’s a richer palette of colors, making the images more lifelike.
Low bit-depth images (like the implied 38): These images exhibit a limited range of colors, resulting in a noticeably blocky and pixelated appearance. Color transitions appear abrupt and uneven, and fine details are lost. The overall visual quality is significantly inferior compared to images with higher bit depths. Think of the difference between a high-resolution photograph and a heavily compressed image on a low-bandwidth internet connection.
The Importance of Context: File Formats and Compression
It's vital to understand that bit depth isn't the only factor determining audio or image quality. The file format and compression techniques used also play a critical role.
Some file formats, like WAV (for audio) and TIFF (for images), are typically uncompressed or use lossless compression methods that preserve all the original data. Others, such as MP3 (audio) and JPEG (images), utilize lossy compression to reduce file size. This compression inevitably discards some data, affecting the final quality. A high bit-depth audio file compressed using a lossy algorithm might still sound inferior to a lower bit-depth audio file using a lossless compression method.
Understanding the Numbers: Addressing the Discrepancy
The numbers "2564" and "38" in the context of bit depth are likely misinterpretations. While 24-bit is a widely used standard, 2564 isn't a recognized bit depth. Similarly, "38" is highly unusual. It's possible that these numbers refer to something other than bit depth (such as a specific file size, compression ratio, or other technical parameter within a specific codec), or are simply errors. It's crucial to always verify the information from reliable sources and consider the context in which these numbers appear.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Can I convert a low bit-depth audio file to a higher bit depth?
A: No, you cannot increase the bit depth of an audio file without introducing artifacts. Information lost during the initial conversion to a low bit depth is irretrievable. You can resample the audio to a higher sample rate, but this won't improve the bit depth.
Q: What is the best bit depth for audio and images?
A: For professional applications and high-quality results, 24-bit audio and 24-bit images (or higher) are recommended. However, 16-bit audio is still widely accepted and provides decent quality for many applications. The choice depends on the specific requirements and intended use.
Q: Does a higher bit depth always mean better quality?
A: Not necessarily. While higher bit depth generally contributes to better quality, other factors like sample rate (for audio), file format, compression methods, and the quality of the source material all play a significant role in the overall quality.
Conclusion: The Significance of Bit Depth in Digital Media
Understanding bit depth is essential for anyone working with digital audio or images. The significant difference between a high bit depth like 24-bit (the likely meaning of 2564) and a very low bit depth like the implied 38 is stark. High bit depth translates to richer detail, wider dynamic range, smoother transitions, and a more faithful representation of the original analog signal. While file size is a consideration, prioritizing bit depth ensures superior quality, especially in professional contexts where preserving detail and fidelity is paramount. Always consider the complete context, including file format and compression, when assessing the overall quality of your digital media. Choosing the right bit depth is a crucial step in ensuring the highest quality results for your audio and visual projects.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 1 4 Of 40
Sep 22, 2025
-
What Is 75 Of 84
Sep 22, 2025
-
What Is 5 Of 11
Sep 22, 2025
-
Write 2 5 As A Decimal
Sep 22, 2025
-
What Equals 16 In Multiplication
Sep 22, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 25 64 Vs 3 8 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.